Next Generation Gold Drugs and Probes: Chemistry and Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 37071737
- PMCID: PMC10317554
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00649
Next Generation Gold Drugs and Probes: Chemistry and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
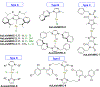
The gold drugs, gold sodium thiomalate (Myocrisin), aurothioglucose (Solganal), and the orally administered auranofin (Ridaura), are utilized in modern medicine for the treatment of inflammatory arthritis including rheumatoid and juvenile arthritis; however, new gold agents have been slow to enter the clinic. Repurposing of auranofin in different disease indications such as cancer, parasitic, and microbial infections in the clinic has provided impetus for the development of new gold complexes for biomedical applications based on unique mechanistic insights differentiated from auranofin. Various chemical methods for the preparation of physiologically stable gold complexes and associated mechanisms have been explored in biomedicine such as therapeutics or chemical probes. In this Review, we discuss the chemistry of next generation gold drugs, which encompasses oxidation states, geometry, ligands, coordination, and organometallic compounds for infectious diseases, cancer, inflammation, and as tools for chemical biology via gold-protein interactions. We will focus on the development of gold agents in biomedicine within the past decade. The Review provides readers with an accessible overview of the utility, development, and mechanism of action of gold-based small molecules to establish context and basis for the thriving resurgence of gold in medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Samuel G. Awuah has patents pending to University of Kentucky Research Foundation.
Figures






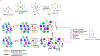
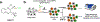



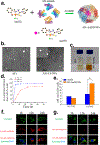
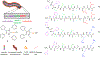


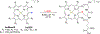

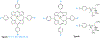




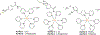
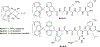
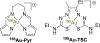
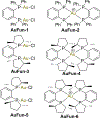



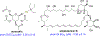
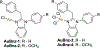
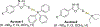
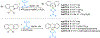

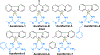
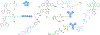
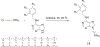
References
-
- Shaw CF Gold-Based Therapeutic Agents. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2589–2600. - PubMed
-
- Barnard PJ; Berners-Price SJ Targeting the Mitochondrial Cell Death Pathway with Gold Compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 1889–1902.
-
- Best SL; Sadler PJ Gold Drugs: Mechanism of Action and Toxicity. Gold Bull. 1996, 29, 87–93.
-
- Dominelli B; Correia JDG; Kühn FE Medicinal Applications of Gold(I/III)-Based Complexes Bearing N-Heterocyclic Carbene and Phosphine Ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 866, 153–164.
-
- Glišić BĐ; Djuran MI Gold Complexes as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview of Different Biological Activities in Relation to the Oxidation State of the Gold Ion and the Ligand Structure. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 5950–5969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

