Avelumab First-Line Maintenance for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma: Results From the JAVELIN Bladder 100 Trial After ≥2 Years of Follow-Up
- PMID: 37071838
- PMCID: PMC10306435
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.01792
Avelumab First-Line Maintenance for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma: Results From the JAVELIN Bladder 100 Trial After ≥2 Years of Follow-Up
Abstract
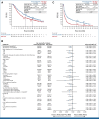
Clinical trials frequently include multiple end points that mature at different times. The initial report, typically based on the primary end point, may be published when key planned coprimary or secondary analyses are not yet available. Clinical Trial Updates provide an opportunity to disseminate additional results from studies, published in JCO or elsewhere, for which the primary end point has already been reported.Initial results from the phase III JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02603432) showed that avelumab first-line (1L) maintenance plus best supportive care (BSC) significantly prolonged overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) versus BSC alone in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma (aUC) who were progression-free after 1L platinum-containing chemotherapy. Avelumab 1L maintenance treatment is now a standard of care for aUC. Here, we report updated data with ≥ 2 years of follow-up in all patients, including OS (primary end point), PFS, safety, and additional novel analyses. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive avelumab plus BSC (n = 350) or BSC alone (n = 350). At data cutoff (June 4, 2021), median follow-up was 38.0 months and 39.6 months, respectively; 67 patients (19.5%) had received ≥2 years of avelumab treatment. OS remained longer with avelumab plus BSC versus BSC alone in all patients (hazard ratio, 0.76 [95% CI, 0.63 to 0.91]; 2-sided P = .0036). Investigator-assessed PFS analyses also favored avelumab. Longer-term safety was consistent with previous analyses; no new safety signals were identified with longer treatment duration. In conclusion, longer-term follow-up continues to show clinically meaningful efficacy benefits with avelumab 1L maintenance plus BSC versus BSC alone in patients with aUC. An interactive visualization of data reported in this article is available.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Powles T, Park SH, Voog E, et al. : Avelumab maintenance therapy for advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med 383:1218-1230, 2020 - PubMed
-
- Cathomas R, Lorch A, Bruins HM, et al. : The 2021 updated European Association of Urology guidelines on metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Eur Urol 81:95-103, 2022 - PubMed
-
- Powles T, Bellmunt J, Comperat E, et al. : Bladder cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 33:244-258, 2022 - PubMed
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Bladder Cancer v1. 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/bladder.pdf
-
- Quan H, Li M, Shih WJ, et al. : Empirical shrinkage estimator for consistency assessment of treatment effects in multi-regional clinical trials. Stat Med 32:1691-1706, 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

