Ventilation failure with elective tracheostomy during oral cancer surgery: a case of tracheal diverticulum
- PMID: 37072301
- PMCID: PMC10124196
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-254134
Ventilation failure with elective tracheostomy during oral cancer surgery: a case of tracheal diverticulum
Abstract
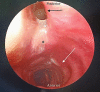
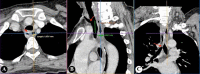
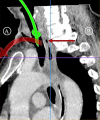
Tracheal diverticulum is usually detected incidentally. Rarely, it may lead to difficulty in securing the airway intraoperatively. Our patient underwent oncological resection under general anaesthesia for advanced oral cancer. Elective tracheostomy was performed at the end of the surgery, and a cuffed tracheostomy tube (T-tube) of 7.5 mm size was inserted through the tracheostoma. Despite repeated attempts at T-tube insertion, ventilation could not be established. However, on advancing the endotracheal tube beyond tracheostoma, ventilation was restored. The T-tube was inserted into the trachea under fibreoptic guidance achieving successful ventilation. A fibreoptic bronchoscopy through the tracheostoma performed after decannulation revealed a mucosalised diverticulum extending behind the posterior wall of the trachea. The bottom of the diverticulum showed mucosa-lined cartilaginous ridge with differentiation into smaller bronchiole-like structures. Tracheal diverticulum should be considered as a possible differential in case of failed ventilation following an otherwise uneventful tracheostomy.
Keywords: Cancer intervention; Ear, nose and throat/otolaryngology; Head and neck cancer; Head and neck surgery.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Infante M, Mattavelli F, Valente M, et al. Tracheal diverticulum: a rare cause and consequence of chronic cough. Eur J Surg 1994;160:315–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
