Effect of school-based nutrition interventions among primary school children in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review protocol
- PMID: 37072365
- PMCID: PMC10124275
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068901
Effect of school-based nutrition interventions among primary school children in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review protocol
Abstract
Introduction: Preadolescents are passing through an intensive growth and development period that will benefit from healthy eating practices. For those attending school, school environments offer several potential benefits and have been demonstrated to influence the quality of dietary intakes and consequentially, nutritional status of school-aged children (SAC). Considering the amount of time children spend in school and the enormous potential of evidence-based interventions, the purpose of this review is to critically appraise peer-reviewed literature addressing the impact of school-based interventions on the nutritional status of SAC aged 6-12 years in sub-Saharan Africa.
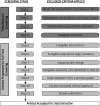
Methods and analysis: A systematic search will be conducted in the following databases and online search records: Medline, CINAHL, Web of Science, Embase, Global health, Global Index Medicus, Cochrane library, Hinari and Google Scholar using search terms and keywords codeveloped with two librarians. An additional search will also be conducted from the reference list of identified literature. Search results of titles and abstracts will be initially screened for eligibility criteria by two independent reviewers and where there is disagreement, a third reviewer will be consulted. Articles meeting these criteria will then undergo a full-text review for the eligibility and exclusion criteria. The Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tool will be used to assess the risk of bias. Data from articles meeting all study criteria will be extracted, analysed and synthesised. A meta-analysis will also be conducted if sufficient data are available.
Ethics and dissemination: This systematic review is limited to publicly accessible data bases not requiring prior ethical approval to access. The results of the systematic review will be disseminated through publications in peer-reviewed journals as well as conference and stakeholder presentations.
Prospero registration number: CRD42022334829.
Keywords: Community child health; Epidemiology; PUBLIC HEALTH.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Menstrual health needs and educational outcomes among adolescent girls living in countries in sub-Saharan Africa: systematic review protocol.BMJ Open. 2025 May 21;15(5):e094613. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-094613. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40398941 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Impact of armed conflicts on HIV treatment outcomes in sub-Saharan Africa: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2023 Aug 9;13(8):e069308. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-069308. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37558447 Free PMC article.
-
Weekly iron-folic acid supplementation and its impact on children and adolescents iron status, mental health and school performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis in sub-Saharan Africa.BMJ Open. 2024 Jun 11;14(6):e084033. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-084033. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38862227 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of primary school-based interventions in improving oral health of children in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Jun 29;22(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02291-2. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 35768801 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of education based on the theory of planned behavior to prevent the consumption of fast food in a population of teenagers.J Health Popul Nutr. 2024 Sep 17;43(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00640-1. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39289771 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of double duty interventions on the frequency of morbidity among adolescents in Debre Berhan Regiopolitan City, Ethiopia: a cluster randomized controlled trial.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 25;25(1):782. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21955-6. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40001035 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kimenju SC, Qaim M. The nutrition transition and indicators of child malnutrition. Food Sec 2016;8:571–83. 10.1007/s12571-016-0566-x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources