The value of ecosystem services in global marine kelp forests
- PMID: 37072389
- PMCID: PMC10113392
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37385-0
The value of ecosystem services in global marine kelp forests
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The value of ecosystem services in global marine kelp forests.Nat Commun. 2023 May 18;14(1):2841. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38666-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37202380 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
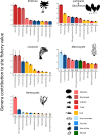
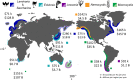
While marine kelp forests have provided valuable ecosystem services for millennia, the global ecological and economic value of those services is largely unresolved. Kelp forests are diminishing in many regions worldwide, and efforts to manage these ecosystems are hindered without accurate estimates of the value of the services that kelp forests provide to human societies. Here, we present a global estimate of the ecological and economic potential of three key ecosystem services - fisheries production, nutrient cycling, and carbon removal provided by six major forest forming kelp genera (Ecklonia, Laminaria, Lessonia, Macrocystis, Nereocystis, and Saccharina). Each of these genera creates a potential value of between $64,400 and $147,100/hectare each year. Collectively, they generate between $465 and $562 billion/year worldwide, with an average of $500 billion. These values are primarily driven by fisheries production (mean $29,900, 904 Kg/Ha/year) and nitrogen removal ($73,800, 657 Kg N/Ha/year), though kelp forests are also estimated to sequester 4.91 megatons of carbon from the atmosphere/year highlighting their potential as blue carbon systems for climate change mitigation. These findings highlight the ecological and economic value of kelp forests to society and will facilitate better informed marine management and conservation decisions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that the authors have no competing interests as defined by Nature Portfolio, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Darwin 1809-1882, C. The Voyage of the Beagle (Dutton, 1959).
-
- Erlandson JM, et al. The kelp highway hypothesis: marine ecology, the coastal migration theory, and the peopling of the Americas. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2007;2:161–174. doi: 10.1080/15564890701628612. - DOI
-
- Thornton TF. The ideology and practice of Pacific herring cultivation among the Tlingit and Haida. Hum. Ecol. 2015;43:213–223. doi: 10.1007/s10745-015-9736-2. - DOI
-
- Kain (Jones), J. M. & Dawes, C. P. Useful European seaweeds: past hopes and present cultivation. Hydrobiologia151, 173–181 (1987).
-
- Peteiro, C. Alginate production from marine macroalgae, with emphasis on kelp farming. In: Alginates and their Biomedical Applications (eds Rehm, B. H. A. & Moradali, M. F.) 27–66 (Springer, 2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

