Diacerein versus non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 37072810
- PMCID: PMC10114432
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-023-03786-6
Diacerein versus non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a common musculoskeletal condition affecting millions of people worldwide and posing a significant challenge to clinicians and researchers. Emerging evidence suggests that the multifaceted symptomatology of KOA may be alleviated by diacerein. With this in mind, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of diacerein in patients with KOA.
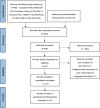
Methods: We systematically searched Embase, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM), Wanfang Database (WanFang), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and China Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP) from their inception to August 2022 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of diacerein intervention on patients with KOA. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of eligible studies and the extraction of relevant data. The meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4 and R 4.1.3 software tools. Depending on the type of outcome indicator selected, summary measures were expressed as mean differences (MD), standardized mean differences (SMD), or odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
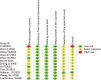
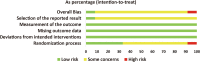
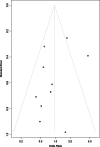
Results: Twelve RCTs with 1732 patients were included. The results revealed that diacerein had comparable efficacy to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in reducing pain indicators such as Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) (SMD = 0.09, 95% CI [-0.10, 0.28], P = 0.34) and visual analogue scale (VAS) (SMD = -0.19, 95% CI [-0.65, 0.27], P = 0.42). However, diacerein outperformed NSAIDs in terms of global efficacy assessment by both patients and investigators (patients: 1.97, 95% CI [1.18, 3.29], P = 0.01; investigator: 2.18, 95% CI [0.99, 4.81], P = 0.05) at the end of treatment and sustained effectiveness in reducing WOMAC score and VAS score at four weeks after treatment. Moreover, there was no significant difference in adverse events incidence between the diacerein and NSAID groups. However, the GRADE evaluation indicated that the majority of the evidence quality was low.
Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that diacerein could potentially be considered as a pharmacological agent with significant efficacy for the treatment of patients suffering from KOA, offering a potential alternative treatment strategy for those patients contraindicated to NSAIDs. However, further high-quality studies with longer follow-up are needed to make more informed decisions about its efficacy in the treatment of KOA.
Keywords: Diacerein; Knee osteoarthritis; Meta-analysis; Systematic review.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

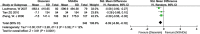

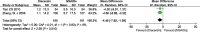
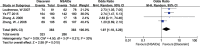
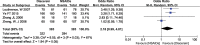

Similar articles
-
The efficacy and safety of Jinwu Gutong capsule in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115247. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115247. Epub 2022 Apr 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35390472 Review.
-
Efficacy, residual effectiveness and safety of diacerein in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 18;101(46):e31700. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031700. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36401382 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Chinese Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 56 Randomized Controlled Trials.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 7;2022:6887988. doi: 10.1155/2022/6887988. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35035664 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness and Safety of Moxibustion for Treating Knee Osteoarthritis: A PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Pain Res Manag. 2019 Dec 17;2019:2653792. doi: 10.1155/2019/2653792. eCollection 2019. Pain Res Manag. 2019. PMID: 31949547 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of controlled clinical studies with diacerein in the treatment of osteoarthritis.Arch Intern Med. 2006 Sep 25;166(17):1899-906. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.17.1899. Arch Intern Med. 2006. PMID: 17000948
Cited by
-
Diacerein ameliorates amiodarone-induced pulmonary fibrosis via targeting the TGFβ1/α-SMA/Smad3 pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):4111-4122. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03450-8. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39417843 Free PMC article.
-
Diacerein and myo-inositol alleviate letrozole-induced PCOS via modulation of HMGB1, SIRT1, and NF-kB: A comparative study.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):4179-4197. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03497-7. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39432066 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of generic versus branded diacerein for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized control trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 6;103(49):e40810. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040810. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39654215 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Similar efficacy of intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections and other biologically active injections in patients with early stages knee osteoarthritis: a level I meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Dec 18;145(1):68. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05614-w. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 39694921
-
Efficacy and safety of diacerein and celecoxib combination therapy for knee osteoarthritis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled prospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 29;102(39):e35317. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035317. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37773836 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

