Visual detection of tropomyosin, a major shrimp allergenic protein using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)-assisted colorimetric aptasensor
- PMID: 37073291
- PMCID: PMC10077205
- DOI: 10.1007/s42995-020-00085-5
Visual detection of tropomyosin, a major shrimp allergenic protein using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)-assisted colorimetric aptasensor
Abstract
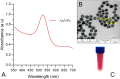
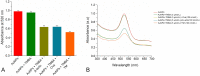
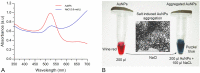
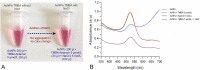
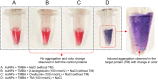
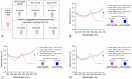
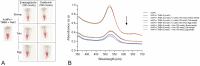
A gold nanoparticle-based label-free colorimetric assay was developed to detect the shrimp allergenic protein tropomyosin (TM), an important biomarker responsible for severe clinical reactivity to shellfish. In a gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)-tropomyosin-binding aptamer (TMBA) complex, the aptamer adsorbs onto the surface of AuNPs and dissociates in the presence of TM. In addition, AuNPs tend to aggregate in the presence of ionic salt, revealing a color change (i.e., wine-red to purple/blue) with a shift in the maximum absorption peak from 520 nm. In the presence of specific binding TM, the aptamer folds into a tertiary structure where it more efficiently stabilizes AuNPs toward the salt-induced aggregation with a hypsochromic shift in the absorption spectra compared to the stabilized AuNPs by aptamer alone. Based on the aggregation and sensitive spectral transformation principle, the AuNPs-based colorimetric aptasensor was successfully applied to detect TM with a range of 10-200 nmol/L and a low detection limit of 40 nmol/L in water samples. The reliability, selectivity, and sensitivity of the aptasensor was then tested with food samples spiked with TM. The observed detection limit was as low as 70 nmol/L in shrimp, 90 nmol/L in tofu, and 80 nmol/L in eggs, respectively. We anticipate the proposed AuNPs-based colorimetric aptasensor assay possesses a high potential for the easy and efficient visual colorimetric detection of TM.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s42995-020-00085-5.
Keywords: Aggregation; Aptamer; Colorimetric assay; Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs); Shellfish allergenic protein; Shrimp tropomyosin (TM).
© Ocean University of China 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Simultaneous and rapid determination of malachite green and leucomalachite green by a label-free colorimetric aptasensor].Se Pu. 2020 Nov 8;38(11):1332-1339. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.04010. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213105 Chinese.
-
Novel colorimetric aptasensor based on unmodified gold nanoparticle and ssDNA for rapid and sensitive detection of T-2 toxin.Food Chem. 2021 Jun 30;348:129128. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129128. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33516992
-
Colorimetric determination of ofloxacin using unmodified aptamers and the aggregation of gold nanoparticles.Mikrochim Acta. 2018 Jul 3;185(7):355. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-2895-2. Mikrochim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29971570
-
Detection of Malachite Green using a colorimetric aptasensor based on the inhibition of the peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoparticles by cetyltrimethylammonium ions.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 May 2;186(5):322. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3436-3. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31049692
-
Gold Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Strategies for Chemical and Biological Sensing Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Jun 6;9(6):861. doi: 10.3390/nano9060861. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31174348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enrofloxacin Rapid Detection in Aquatic Foods: Based on DNA Aptamer Sensor.Foods. 2024 Mar 20;13(6):941. doi: 10.3390/foods13060941. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38540931 Free PMC article.
-
A Label-Free Gold Nanoparticles-Based Optical Aptasensor for the Detection of Retinol Binding Protein 4.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;12(12):1061. doi: 10.3390/bios12121061. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amendola V, Meneghetti M, Stener M, Guo Y, Chen S, Crespo P, García MA, Hernando A, Pengo P, Pasquato L. Physico-chemical characteristics of gold nanoparticles. Compr Anal Chem. 2014;66:81–152. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63285-2.00003-1. - DOI
-
- António M, Ferreira R, Vitorino R, Daniel-da-Silva AL (2020) A simple aptamer-based colorimetric assay for rapid detection of C-reactive protein using gold nanoparticles. Talanta: 120868 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

