One cell at a time: droplet-based microbial cultivation, screening and sequencing
- PMID: 37073344
- PMCID: PMC10077293
- DOI: 10.1007/s42995-020-00082-8
One cell at a time: droplet-based microbial cultivation, screening and sequencing
Abstract
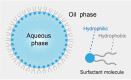
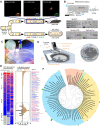
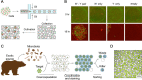
Microbes thrive and, in turn, influence the earth's environment, but most are poorly understood because of our limited capacity to reveal their natural diversity and function. Developing novel tools and effective strategies are critical to ease this dilemma and will help to understand their roles in ecology and human health. Recently, droplet microfluidics is emerging as a promising technology for microbial studies with value in microbial cultivating, screening, and sequencing. This review aims to provide an overview of droplet microfluidics techniques for microbial research. First, some critical points or steps in the microfluidic system are introduced, such as droplet stabilization, manipulation, and detection. We then highlight the recent progress of droplet-based methods for microbiological applications, from high-throughput single-cell cultivation, screening to the targeted or whole-genome sequencing of single cells.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Droplet microfluidics; Microbial cultivation; Single-cell screening; Single-cell sequencing; Uncultured microorganisms.
© Ocean University of China 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare there is no conflict of interest between them.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Droplet Microfluidics for Microbial Biotechnology.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2022;179:129-157. doi: 10.1007/10_2020_140. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 32888037
-
[Application of Droplet-Based Microfluidics in Microbial Research].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May;54(3):673-678. doi: 10.12182/20230560303. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37248604 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Highly parallelized droplet cultivation and prioritization of antibiotic producers from natural microbial communities.Elife. 2021 Mar 25;10:e64774. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64774. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33764297 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet microfluidics: unveiling the hidden complexity of the human microbiome.Lab Chip. 2025 Feb 25;25(5):1128-1148. doi: 10.1039/d4lc00877d. Lab Chip. 2025. PMID: 39775305 Review.
-
Single-cell droplet microfluidics for biomedical applications.Analyst. 2022 May 30;147(11):2294-2316. doi: 10.1039/d1an02321g. Analyst. 2022. PMID: 35506869 Review.
Cited by
-
Dielectrophoresis for Isolating Low-Abundance Bacteria Obscured by Impurities in Environmental Samples.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025 Mar 14;27(2):64. doi: 10.1007/s10126-025-10441-0. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40085294 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-Technologies for Assessing Microbial Dynamics in Controlled Environments.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 28;12:745835. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.745835. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35154021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging microfluidic technologies for microbiome research.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 16;13:906979. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.906979. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36051769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
1-Octanol-assisted ultra-small volume droplet microfluidics with nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 Sep 8;1321:342998. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342998. Epub 2024 Jul 21. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39155094 Free PMC article.
-
Modern Trends in Natural Antibiotic Discovery.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 23;13(5):1073. doi: 10.3390/life13051073. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37240718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Autour A, Ryckelynck M. Ultrahigh-throughput improvement and discovery of enzymes using droplet-based microfluidic screening. Micromachines. 2017;8:128. doi: 10.3390/mi8040128. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

