In vivo hypermutation and continuous evolution
- PMID: 37073402
- PMCID: PMC10108624
- DOI: 10.1038/s43586-022-00130-w
In vivo hypermutation and continuous evolution
Keywords: Cheater mutations; Clonal interference; Consensus sequencing; Directed evolution; Greedy mutations; Hypermutation; Integration cassette; Processivity; Sign epistasis; Unique molecular identifier.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

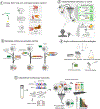
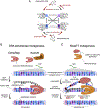
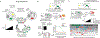


References
-
- Arnold FH Design by Directed Evolution. Acc. Chem. Res 31, 125–131 (1998).
-
- Packer MS & Liu DR Methods for the directed evolution of proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet 16, 379–394 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Chen K & Arnold FH Engineering new catalytic activities in enzymes. Nat. Catal 3, 203–213 (2020).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
