Establishing standards for Yonsei point in a White South African population for the treatment of gummy smile
- PMID: 37073426
- PMCID: PMC10280613
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.735
Establishing standards for Yonsei point in a White South African population for the treatment of gummy smile
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study is to establish the efficacy of Yonsei point in the treatment of a gummy smile in a White South African population. The accurate surface anatomy criteria in relation to the underlying musculature for the administration of Botulinum toxin injections in the treatment of gummy smile was determined.
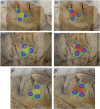
Materials and methods: Nineteen (10 males and 9 females) cadavers were selected for facial dissection. Facial profile photographs were taken before and after dissection. The before and after photographs were overlayed to determine where the pin positions should be on the dissected cadaver to determine the Yonsei point. The levator labii superioris (LLS), LLS alaeque nasi (LLSAN), zygomaticus minor, and zygomaticus major muscles were measured using a protractor and ruler, which accounted for the manual measurements. Digital measurements were measured by importing dissected images into ImageJ. Circles with a 2 cm diameter (1 cm radius) were constructed to determine whether the Yonsei point could successfully influence muscles fibers.
Results: Digital and manual measurements show comparable results with high correlation and reliability. Results showed that the White South African population had narrower facial musculature angles as compared with the Korean population.
Conclusion: Based on the selected sample, the Yonsei point is an ineffective injection site for the successful treatment of gummy smile in a White South African population.
Keywords: Yonsei point; botox injections; hyperactive lip elevator muscles; injection landmark radii.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Agur, A. M. R. , Dalley II, A. F. , & Moore, K. L. (2019). Moore's essential clinical anatomy (6th ed.). Wolters Kluwer.
-
- Al Wayli, H. (2019). Versatility of botulinum toxin at the Yonsei point for the treatment of gummy smile. The International Journal of Esthetic Dentistry, 14(1), 86–95. - PubMed
-
- Bobak, C. A. , Barr, P. J. , & O'Malley, A. J. (2018). Estimation of an inter‐rater intra‐class correlation coefficient that overcomes common assumption violations in the assessment of health measurement scales. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 18(1), 93. 10.1186/s12874-018-0550-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davenport, T. R. H. , & Saunders, C. C. (2000). South Africa: A modern history (5th ed.). Macmillan Press, St. Martin's Press.
-
- Dong, J. K. , Jin, T. H. , Cho, H. W. , & Oh, S. C. (1999). The esthetics of the smile: a review of some recent studies. The International Journal of Prosthodontics, 12(1), 9–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

