Antisense, but not sense, repeat expanded RNAs activate PKR/eIF2α-dependent ISR in C9ORF72 FTD/ALS
- PMID: 37073950
- PMCID: PMC10188109
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.85902
Antisense, but not sense, repeat expanded RNAs activate PKR/eIF2α-dependent ISR in C9ORF72 FTD/ALS
Abstract
GGGGCC (G4C2) hexanucleotide repeat expansion in the C9ORF72 gene is the most common genetic cause of frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The repeat is bidirectionally transcribed and confers gain of toxicity. However, the underlying toxic species is debated, and it is not clear whether antisense CCCCGG (C4G2) repeat expanded RNAs contribute to disease pathogenesis. Our study shows that C9ORF72 antisense C4G2 repeat expanded RNAs trigger the activation of the PKR/eIF2α-dependent integrated stress response independent of dipeptide repeat proteins that are produced through repeat-associated non-AUG-initiated translation, leading to global translation inhibition and stress granule formation. Reducing PKR levels with either siRNA or morpholinos mitigates integrated stress response and toxicity caused by the antisense C4G2 RNAs in cell lines, primary neurons, and zebrafish. Increased phosphorylation of PKR/eIF2α is also observed in the frontal cortex of C9ORF72 FTD/ALS patients. Finally, only antisense C4G2, but not sense G4C2, repeat expanded RNAs robustly activate the PKR/eIF2α pathway and induce aberrant stress granule formation. These results provide a mechanism by which antisense C4G2 repeat expanded RNAs elicit neuronal toxicity in FTD/ALS caused by C9ORF72 repeat expansions.
Keywords: C9ORF72; FTD/ALS; PKR; antisense RNA; integrated stress response; neuroscience; zebrafish.
© 2023, Parameswaran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JP, NZ, EB, KT, DP, KY, SA, KH, AB, ED, SS, GC, GB, LV, JJ No competing interests declared
Figures


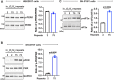

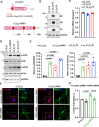




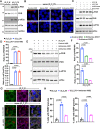
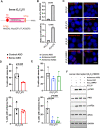



Update of
References
-
- Aladesuyi Arogundade O, Stauffer JE, Saberi S, Diaz-Garcia S, Malik S, Basilim H, Rodriguez MJ, Ohkubo T, Ravits J. Antisense RNA foci are associated with nucleoli and TDP-43 mislocalization in c9orf72-ALS/FTD: a quantitative study. Acta Neuropathologica. 2019;137:527–530. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-01955-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ash PEA, Bieniek KF, Gendron TF, Caulfield T, Lin W-L, DeJesus-Hernandez M, van Blitterswijk MM, Jansen-West K, Paul JW, III, Rademakers R, Boylan KB, Dickson DW, Petrucelli L. Unconventional translation of C9orf72 GGGGCC expansion generates insoluble polypeptides specific to c9FTD/ALS. Neuron. 2013;77:639–646. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atanasio A, Decman V, White D, Ramos M, Ikiz B, Lee H-C, Siao C-J, Brydges S, LaRosa E, Bai Y, Fury W, Burfeind P, Zamfirova R, Warshaw G, Orengo J, Oyejide A, Fralish M, Auerbach W, Poueymirou W, Freudenberg J, Gong G, Zambrowicz B, Valenzuela D, Yancopoulos G, Murphy A, Thurston G, Lai K-MV. C9Orf72 ablation causes immune dysregulation characterized by leukocyte expansion, autoantibody production and glomerulonephropathy in mice. Scientific Reports. 2016;6:23204. doi: 10.1038/srep23204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boeynaems S, Bogaert E, Michiels E, Gijselinck I, Sieben A, Jovičić A, De Baets G, Scheveneels W, Steyaert J, Cuijt I, Verstrepen KJ, Callaerts P, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C, Van Damme P, Gitler AD, Robberecht W, Van Den Bosch L. Drosophila screen connects nuclear transport genes to Dpr pathology in c9als/FTD. Scientific Reports. 2016;6:20877. doi: 10.1038/srep20877. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

