Status of major hemostatic components in the setting of COVID-19: the effect on endothelium, platelets, coagulation factors, fibrinolytic system, and complement
- PMID: 37074380
- PMCID: PMC10115391
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-023-05234-1
Status of major hemostatic components in the setting of COVID-19: the effect on endothelium, platelets, coagulation factors, fibrinolytic system, and complement
Abstract
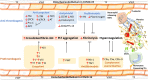
The coagulation, fibrinolytic, anticoagulation, and complement systems are in delicate balance with the vessel wall endothelium ensuring appropriate hemostasis. Coagulopathy in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is not a simple disorder of one hemostatic component but a complicated process affecting most of the hemostasis system. COVID-19 disturbs the balance between the procoagulant systems and the regulatory mechanisms. Here, we investigate the effect of COVID-19 on key hemostatic components, including platelets, endothelial cells, coagulation factors, fibrinolytic system, anticoagulant protein system, and complement system, to improve our understanding of the pathophysiological processes underlying COVID-19 coagulopathy based on evidence.
Keywords: Blood platelets; COVID-19; Endothelium; Fibrinolysis; Hemostasis; Thrombosis.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Procoagulant activity in hemostasis and thrombosis: Virchow's triad revisited.Anesth Analg. 2012 Feb;114(2):275-85. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31823a088c. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Anesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22104070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experiences in Routine Genetic Analysis of Hereditary Hemorrhagic, Thrombotic, and Platelet Disorders.Hamostaseologie. 2022 Oct;42(S 01):S5-S12. doi: 10.1055/a-1726-4793. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Hamostaseologie. 2022. PMID: 35226963 Review.
-
Haemostatic changes and the oral contraceptive pill.Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1997 Sep;11(3):545-64. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3552(97)80027-2. Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1997. PMID: 9488791 Review.
-
New fundamentals in hemostasis.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jan;93(1):327-58. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00016.2011. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23303912 Review.
-
An overview of hemostasis.Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1988 Jan;18(1):5-20. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(88)50003-7. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1988. PMID: 3282384 Review.
Cited by
-
Aprotinin (I): Understanding the Role of Host Proteases in COVID-19 and the Importance of Pharmacologically Regulating Their Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 10;25(14):7553. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147553. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of COVID-19 on hemostasis: coagulation abnormalities and management perspectives.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jul 2;86(10):5844-5850. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002237. eCollection 2024 Oct. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39359765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesomycoplasma hyopneumoniae lipoprotein Mhp390 serves as a plasminogen receptor mediating extracellular matrix degradation and respiratory epithelial cells injury.Vet Res. 2025 Jun 21;56(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01551-7. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40544247 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and the Concept of Thrombo-Inflammation: Review of the Relationship between Immune Response, Endothelium and Coagulation.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 23;12(23):7245. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237245. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunity and Coagulation in COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 19;25(20):11267. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011267. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

