Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibition in Parkinson's Disease: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 37074485
- PMCID: PMC11410141
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-023-01349-1
Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibition in Parkinson's Disease: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
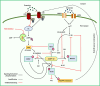
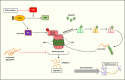
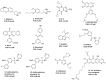
Clinicians and researchers are exploring safer and novel treatment strategies for treating the ever-prevalent Parkinson's disease (PD) across the globe. Several therapeutic strategies are used clinically for PD, including dopamine replacement therapy, DA agonists, MAO-B blockers, COMT blockers, and anticholinergics. Surgical interventions such as pallidotomy, particularly deep brain stimulation (DBS), are also employed. However, they only provide temporal and symptomatic relief. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is one of the secondary messengers involved in dopaminergic neurotransmission. Phosphodiesterase (PDE) regulates cAMP and cGMP intracellular levels. PDE enzymes are subdivided into families and subtypes which are expressed throughout the human body. PDE4 isoenzyme- PDE4B subtype is overexpressed in the substantia nigra of the brain. Various studies have implicated multiple cAMP-mediated signaling cascades in PD, and PDE4 is a common link that can emerge as a neuroprotective and/or disease-modifying target. Furthermore, a mechanistic understanding of the PDE4 subtypes has provided perceptivity into the molecular mechanisms underlying the adverse effects of phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors (PDE4Is). The repositioning and development of efficacious PDE4Is for PD have gained much attention. This review critically assesses the existing literature on PDE4 and its expression. Specifically, this review provides insights into the interrelated neurological cAMP-mediated signaling cascades involving PDE4s and the potential role of PDE4Is in PD. In addition, we discuss existing challenges and possible strategies for overcoming them.
Keywords: Allosteric modulation; Neurodegeneration; PDE4; PDE4 inhibitors; Parkinson’s disease; cAMP.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting phosphodiesterase 4 as a potential therapy for Parkinson's disease: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Apr 15;51(1):510. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09484-8. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38622307 Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase-4 enzyme as a therapeutic target in neurological disorders.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Oct;160:105078. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105078. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32673703 Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and neurological disorders: A promising frontier in neuropharmacology.Adv Pharmacol. 2025;102:159-209. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2024.10.005. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Adv Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39929579 Review.
-
Modulation of Second Messenger Signaling in the Brain Through PDE4 and PDE5 Inhibition: Therapeutic Implications for Neurological Disorders.Cells. 2025 Jan 9;14(2):86. doi: 10.3390/cells14020086. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond PDE4 inhibition: A comprehensive review on downstream cAMP signaling in the central nervous system.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Aug;177:117009. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117009. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38908196 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphodiesterase inhibition and Gucy2C activation enhance tyrosine hydroxylase Ser40 phosphorylation and improve 6-hydroxydopamine-induced motor deficits.Cell Biosci. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01312-7. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39456033 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-PKA/EPAC signaling and cancer: the interplay in tumor microenvironment.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jan 17;17(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01524-x. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38233872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Azaindole Compounds as Phosphodiesterase 4B Inhibitors for Treating Immune-Inflammatory Diseases or Disorders.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025 Apr 7;16(5):717-718. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5c00158. eCollection 2025 May 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 40365387
-
Adenylyl Cyclases as Therapeutic Targets in Neuroregeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 25;26(13):6081. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136081. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Phosphodiesterase 4 Suppresses Neuronal Ferroptosis After Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Mar;62(3):3376-3395. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04495-9. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39287745
References
-
- Abdulrahim H, Thistleton S, Adebajo AO et al (2015) Apremilast: a PDE4 inhibitor for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 10.1517/14656566.2015.1034107 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez R, Sette C, Yang D, et al (1995) Activation and selective inhibition of a cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase, PDE-4D3. Mol Pharmacol - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

