Time-dependent regulation of cytokine production by RNA binding proteins defines T cell effector function
- PMID: 37074914
- PMCID: PMC10242446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112419
Time-dependent regulation of cytokine production by RNA binding proteins defines T cell effector function
Abstract
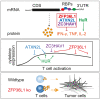
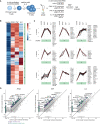
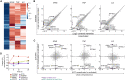
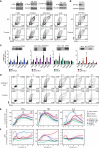
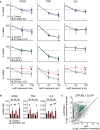
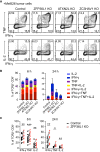
Potent T cell responses against infections and malignancies require a rapid yet tightly regulated production of toxic effector molecules. Their production level is defined by post-transcriptional events at 3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs). RNA binding proteins (RBPs) are key regulators in this process. With an RNA aptamer-based capture assay, we identify >130 RBPs interacting with IFNG, TNF, and IL2 3' UTRs in human T cells. RBP-RNA interactions show plasticity upon T cell activation. Furthermore, we uncover the intricate and time-dependent regulation of cytokine production by RBPs: whereas HuR supports early cytokine production, ZFP36L1, ATXN2L, and ZC3HAV1 dampen and shorten the production duration, each at different time points. Strikingly, even though ZFP36L1 deletion does not rescue the dysfunctional phenotype, tumor-infiltrating T cells produce more cytokines and cytotoxic molecules, resulting in superior anti-tumoral T cell responses. Our findings thus show that identifying RBP-RNA interactions reveals key modulators of T cell responses in health and disease.
Keywords: ATXN2L; CP: Immunology; HuR; RNA binding proteins; ZC3HAV1; ZFP36L1; cytokines; human T cells; post-transcriptional regulation; tumor-infiltrating T cells.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Almeida J.R., Price D.A., Papagno L., Arkoub Z.A., Sauce D., Bornstein E., Asher T.E., Samri A., Schnuriger A., Theodorou I., et al. Superior control of HIV-1 replication by CD8+ T cells is reflected by their avidity, polyfunctionality, and clonal turnover. J. Exp. Med. 2007;204:2473–2485. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070784. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciuffreda D., Comte D., Cavassini M., Giostra E., Bühler L., Perruchoud M., Heim M.H., Battegay M., Genné D., Mulhaupt B., et al. Polyfunctional HCV-specific T-cell responses are associated with effective control of HCV replication. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008;38:2665–2677. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838336. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Quezada S.A., Simpson T.R., Peggs K.S., Merghoub T., Vider J., Fan X., Blasberg R., Yagita H., Muranski P., Antony P.A., et al. Tumor-reactive CD4+ T cells develop cytotoxic activity and eradicate large established melanoma after transfer into lymphopenic hosts. J. Exp. Med. 2010;207:637–650. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091918. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

