Multiple tethers of organelle contact sites are involved in α-synuclein toxicity in yeast
- PMID: 37074954
- PMCID: PMC10398879
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E23-01-0029
Multiple tethers of organelle contact sites are involved in α-synuclein toxicity in yeast
Abstract
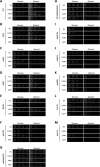
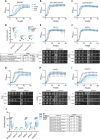
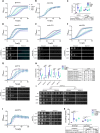
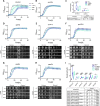
The protein α-synuclein (α-syn) is one of the major factors linked to Parkinson's disease, yet how its misfolding and deposition contribute to the pathology remains largely elusive. Recently, contact sites among organelles were implicated in the development of this disease. Here, we used the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, in which organelle contact sites have been characterized extensively, as a model to investigate their role in α-syn cytotoxicity. We observed that lack of specific tethers that anchor the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane resulted in cells with increased resistance to α-syn expression. Additionally, we found that strains lacking two dual-function proteins involved in contact sites, Mdm10 and Vps39, were resistant to the expression of α-syn. In the case of Mdm10, we found that this is related to its function in mitochondrial protein biogenesis and not to its role as a contact site tether. In contrast, both functions of Vps39, in vesicular transport and as a tether of the vacuole-mitochondria contact site, were required to support α-syn toxicity. Overall, our findings support that interorganelle communication through membrane contact sites is highly relevant for α-syn-mediated toxicity.
Figures
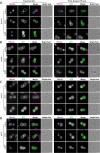
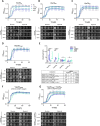
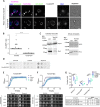
Similar articles
-
Vps39 is required for ethanolamine-stimulated elevation in mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Jun;1865(6):158655. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158655. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32058032 Free PMC article.
-
Vps39 Interacts with Tom40 to Establish One of Two Functionally Distinct Vacuole-Mitochondria Contact Sites.Dev Cell. 2018 Jun 4;45(5):621-636.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.05.011. Dev Cell. 2018. PMID: 29870720
-
Compounds from an unbiased chemical screen reverse both ER-to-Golgi trafficking defects and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease models.Dis Model Mech. 2010 Mar-Apr;3(3-4):194-208. doi: 10.1242/dmm.004267. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Dis Model Mech. 2010. PMID: 20038714 Free PMC article.
-
Organelle contact zones as sites for lipid transfer.J Biochem. 2019 Feb 1;165(2):115-123. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvy088. J Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30371789 Review.
-
Mitochondria-organelle contact sites: the plot thickens.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Apr 15;45(2):477-488. doi: 10.1042/BST20160130. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28408488 Review.
Cited by
-
Shape Matters: The Utility and Analysis of Altered Yeast Mitochondrial Morphology in Health, Disease, and Biotechnology.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;26(5):2152. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052152. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amado L, Cogan AP, González Montoro A (2023). Tethering proteins of the same contact site affect the localization and mobility of each other. J Cell Sci in press. - PubMed
-
- Babazadeh R, Ahmadpour D, Jia S, Hao X, Widlund P, Schneider K, Eisele F, Edo LD, Smits GJ, Liu B, Nystrom T (2019). Syntaxin 5 is required for the formation and clearance of protein inclusions during proteostatic stress. Cell Rep 28, 2096–2110.e8. - PubMed
-
- Balderhaar HJ, Ungermann C (2013). CORVET and HOPS tethering complexes—coordinators of endosome and lysosome fusion. J Cell Sci 126, 1307–1316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

