Exposure to quasi-ultrafine particulate matter accelerates memory impairment and Alzheimer's disease-like neuropathology in the AppNL-G-F knock-in mouse model
- PMID: 37074955
- PMCID: PMC10230292
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfad036
Exposure to quasi-ultrafine particulate matter accelerates memory impairment and Alzheimer's disease-like neuropathology in the AppNL-G-F knock-in mouse model
Abstract
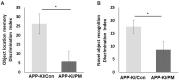
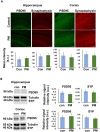
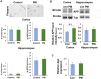
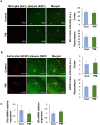
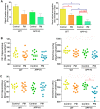
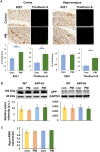
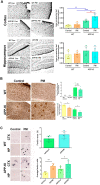
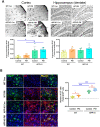
Exposure to traffic-related air pollution consisting of particulate matter (PM) is associated with cognitive decline leading to Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, we sought to examine the neurotoxic effects of exposure to ultrafine PM and how it exacerbates neuronal loss and AD-like neuropathology in wildtype (WT) mice and a knock-in mouse model of AD (AppNL-G-F/+-KI) when the exposure occurs at a prepathologic stage or at a later age with the presence of neuropathology. AppNL-G-F/+-KI and WT mice were exposed to concentrated ultrafine PM from local ambient air in Irvine, California, for 12 weeks, starting at 3 or 9 months of age. Particulate matter-exposed animals received concentrated ultrafine PM up to 8 times above the ambient levels, whereas control animals were exposed to purified air. Particulate matter exposure resulted in a marked impairment of memory tasks in prepathologic AppNL-G-F/+-KI mice without measurable changes in amyloid-β pathology, synaptic degeneration, and neuroinflammation. At aged, both WT and AppNL-G-F/+-KI mice exposed to PM showed a significant memory impairment along with neuronal loss. In AppNL-G-F/+-KI mice, we also detected an increased amyloid-β buildup and potentially harmful glial activation including ferritin-positive microglia and C3-positive astrocytes. Such glial activation could promote the cascade of degenerative consequences in the brain. Our results suggest that exposure to PM impairs cognitive function at both ages while exacerbation of AD-related pathology and neuronal loss may depend on the stage of pathology, aging, and/or state of glial activation. Further studies will be required to unveil the neurotoxic role of glial activation activated by PM exposure.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; air pollution; inflammation; mouse model; neuronal loss.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of concentrated ambient ultrafine particulate matter on hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease in the 3xTgAD mouse model.Neurotoxicology. 2021 May;84:172-183. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2021.03.010. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Neurotoxicology. 2021. PMID: 33794265 Free PMC article.
-
Selective memory and behavioral alterations after ambient ultrafine particulate matter exposure in aged 3xTgAD Alzheimer's disease mice.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019 Nov 26;16(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12989-019-0323-3. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31771615 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal choline supplementation prevents learning and memory deficits and reduces brain amyloid Aβ42 deposition in AppNL-G-F Alzheimer's disease model mice.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 5;19(2):e0297289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297289. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38315685 Free PMC article.
-
PM2.5 exposure in association with AD-related neuropathology and cognitive outcomes.Environ Pollut. 2022 Jan 1;292(Pt A):118320. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118320. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 34634399 Review.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
Cited by
-
Air Pollution as an Environmental Risk Factor for Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias.Med Res Arch. 2024 Oct;12(10):5825. doi: 10.18103/mra.v12i10.5825. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Med Res Arch. 2024. PMID: 39822906 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Caused by Noise and Air Pollution-Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;13(3):266. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030266. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Air pollution amyloidogenesis is attenuated by the gamma-secretase modulator GSM-15606.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Sep;20(9):6107-6114. doi: 10.1002/alz.14086. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39132765 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

