Grambank reveals the importance of genealogical constraints on linguistic diversity and highlights the impact of language loss
- PMID: 37075104
- PMCID: PMC10115409
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg6175
Grambank reveals the importance of genealogical constraints on linguistic diversity and highlights the impact of language loss
Abstract
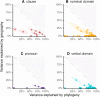
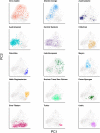
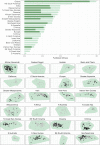
While global patterns of human genetic diversity are increasingly well characterized, the diversity of human languages remains less systematically described. Here, we outline the Grambank database. With over 400,000 data points and 2400 languages, Grambank is the largest comparative grammatical database available. The comprehensiveness of Grambank allows us to quantify the relative effects of genealogical inheritance and geographic proximity on the structural diversity of the world's languages, evaluate constraints on linguistic diversity, and identify the world's most unusual languages. An analysis of the consequences of language loss reveals that the reduction in diversity will be strikingly uneven across the major linguistic regions of the world. Without sustained efforts to document and revitalize endangered languages, our linguistic window into human history, cognition, and culture will be seriously fragmented.
Figures

References
-
- H. Hammarström, R. Forkel, M. Haspelmath, S. Bank, glottolog/glottolog: Glottolog Database 4.5 as CLDF (v4.5) [Data set] (Zenodo, 2021); 10.5281/zenodo.5772649. - DOI
-
- M. H. Christiansen, N. Chater,Language as shaped by the brain. Behav. Brain Sci. 31, 489–509 (2008). - PubMed
-
- J. Nichols, Linguistic Diversity in Space and Time (University of Chicago Press, 1992).
-
- P. Muysken, From Linguistic Areas to Areal Linguistics (John Benjamins, 2008).

