Magnetic resonance arthrographic demonstration of extension of labral defects in paraglenoid labral cysts
- PMID: 37075440
- PMCID: PMC10176652
- DOI: 10.1590/1806-9282.20221019
Magnetic resonance arthrographic demonstration of extension of labral defects in paraglenoid labral cysts
Abstract
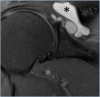
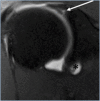
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the extension of labral tears associated with paraglenoid labral cysts by magnetic resonance arthrography.
Methods: The magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance arthrography images of patients with paraglenoid labral cysts who presented to our clinic between 2016 and 2018 were examined. In patients with paraglenoid labral cysts, the location of the cysts, the relation between the cyst and the labrum, the location and extent of glenoid labrum damage, and whether there was contrast medium passage into the cysts were investigated. The accuracy of magnetic resonance arthrographic information was evaluated in patients undergoing arthroscopy.
Results: In this prospective study, a paraglenoid labral cyst was detected in 20 patients. In 16 patients, there was a defect in the labrum adjacent to the cyst. Seven of these cysts were adjacent to the posterior superior labrum. In 13 patients, there were contrast solution leak into the cyst. For the remaining seven patients, no contrast-medium passage was observed in the cyst. Three patients had sublabral recess anomalies. Two patients had rotator cuff muscle denervation atrophy accompanying the cysts. The cysts of these patients were larger compared to those of the other patients.
Conclusion: Paraglenoid labral cysts are frequently associated with the rupture of the adjacent labrum. In these patients, symptoms are generally accompanied by secondary labral pathologies. Magnetic resonance arthrography can be successfully used not only to demonstrate the association of the cyst with the joint capsule and labrum, but also to reliably demonstrate the presence and extension of labral defects.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: the authors declare there is no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MR arthrographic evaluation of posterior paraglenoid labral cysts: a retrospective study.Acta Radiol. 2020 Jun;61(6):789-795. doi: 10.1177/0284185119883389. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Acta Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31653186
-
Humeral Chondral Defect and Labral Tear Associated with Paraglenoid Labral Cyst: A Case Report.Med Princ Pract. 2016;25(5):488-90. doi: 10.1159/000447669. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Med Princ Pract. 2016. PMID: 27318468 Free PMC article.
-
MR imaging and MR arthrography of paraglenoid labral cysts.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Jun;174(6):1707-15. doi: 10.2214/ajr.174.6.1741707. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. PMID: 10845511
-
Magnetic resonance arthrography of the labral-ligamentous complex of the shoulder: an update.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2002 Sep;31(5):614-20. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2002. PMID: 12395648 Review.
-
The use of ultrasound in the assessment of the glenoid labrum of the glenohumeral joint. Part II: Examples of labral pathologies.J Ultrason. 2012 Sep;12(50):329-41. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2012.0018. Epub 2012 Sep 30. J Ultrason. 2012. PMID: 26672471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

