Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 Enhances Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in Severe Asthma
- PMID: 37075799
- PMCID: PMC10359643
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2023.15.4.451
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 Enhances Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in Severe Asthma
Abstract
Purpose: Severe asthma (SA) is characterized by persistent airway inflammation and remodeling, followed by lung function decline. The present study aimed to evaluate the role of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in the pathogenesis of SA.
Methods: We enrolled 250 adult asthmatics (54 with SA and 196 with non-SA) and 140 healthy controls (HCs). Serum TIMP-1 levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The release of TIMP-1 from airway epithelial cells (AECs) in response to stimuli as well as the effects of TIMP-1 on the activations of eosinophils and macrophages were evaluated in vitro and in vivo.
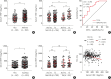
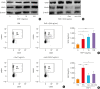
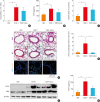
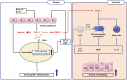
Results: Significantly higher levels of serum TIMP-1 were noted in asthmatics than in HCs, in the SA group than in non-SA group, and in the type 2 SA group than in non-type 2 SA group (P < 0.01 for all). A negative correlation between serum TIMP-1 and FEV1% values (r = -0.400, P = 0.003) was noted in the SA group. In vitro study demonstrated that TIMP-1 was released from AECs in response to poly I:C, IL-13, eosinophil extracellular traps (EETs) and in coculture with eosinophils. TIMP-1-stimulated mice showed eosinophilic airway inflammation, which was not completely suppressed by steroid treatment. In vitro and in vivo functional studies showed that TIMP-1 directly activated eosinophils and macrophages, and induced the release of EETs and macrophages to polarize toward M2 subset, which was suppressed by anti-TIMP-1 antibody.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that TIMP-1 enhances eosinophilic airway inflammation and that serum TIMP-1 may be a potential biomarker and/or therapeutic target for type 2 SA.
Keywords: Asthma; TIMP-1; airway remodeling; eosinophils; epithelial cells; inflammation; macrophages.
Copyright © 2023 The Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology • The Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interests.
Figures




References
-
- Woo SD, Yang EM, Jang J, Lee Y, Shin YS, Ye YM, et al. Serum-free immunoglobulin E: a useful biomarker of atopy and type 2 asthma in adults with asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;127:109–115.e1. - PubMed
-
- Nair P, Surette MG, Virchow JC. Neutrophilic asthma: misconception or misnomer? Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9:441–443. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Park Y, Kim C, Lee E, Lee HY, Woo SD, et al. Longitudinal outcomes of severe asthma: real-world evidence of multidimensional analyses. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:1285–1294.e6. - PubMed

