Healthcare utilisation and costs associated with adherence to antipsychotics among people living with HIV/AIDS and schizophrenia: a population-based cohort study in British Columbia, Canada
- PMID: 37076145
- PMCID: PMC10124256
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070680
Healthcare utilisation and costs associated with adherence to antipsychotics among people living with HIV/AIDS and schizophrenia: a population-based cohort study in British Columbia, Canada
Abstract
Objectives: Non-adherence to antipsychotics is the greatest obstacle to treating schizophrenia. We assessed the economic and clinical impacts of adherence to antipsychotics among people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWH) and schizophrenia in British Columbia, Canada.
Design and setting: A population-based cohort study in British Columbia, Canada.
Methods: Eligible PLWH were enrolled in the Seek and Treat for Optimal Prevention HIV/AIDS population-based cohort during 2001-2016, diagnosed with schizophrenia, on antipsychotics for ≥1 day, and followed for ≥1 year from schizophrenia diagnosis date or 1 January 2001, whichever occurred last.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: A two-part model assessed the marginal effect of adherence on healthcare costs (in 2016 Canadian dollar), while logistic regression examined the effect on virological failure, and generalised linear mixed models examined the effect on hospital readmissions within 30 days and length of hospital stay.
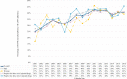
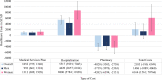
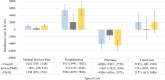
Results: Among 726 PLWH with schizophrenia, ≥80% adherence to antipsychotics increased from 25% (50/198) in 2001 to 41% (225/554) in 2016. In most years, we observed no difference in adherence to antipsychotics among those who used only injectables, only non-injectables, and a combination of both, or among those who have ever consumed typical/first-generation antipsychotics and who consumed only atypical/second-generation antipsychotics. Overall healthcare costs were higher in the non-adherent group ($C2185), driven by the average annual hospitalisation costs ($C5517), particularly among women ($C8806) and people who ever injected drugs (PWID) ($C5985). Non-adherent individuals also experienced higher hospital readmissions (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 1.48, 95% CI 1.23 to 1.77), and longer hospital stays (adjusted mean ratio 1.23, 95% CI 1.13 to 1.35) in comparison to adherent individuals. We found no difference in virological failure by adherence groups, except when we stratified by gender where the aOR for women was 2.48 (95% CI 1.06 to 5.82).
Conclusions: Our results showed that implementing strategies and interventions to increase antipsychotic adherence, particularly among women and PWID, will be critical in addressing this public health challenge.
Keywords: EPIDEMIOLOGY; HIV & AIDS; PUBLIC HEALTH; Schizophrenia & psychotic disorders; THERAPEUTICS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JSGM: Institutional grants have been provided by Gilead, Merck and ViiV Healthcare. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
