Disrupting the α-synuclein-ESCRT interaction with a peptide inhibitor mitigates neurodegeneration in preclinical models of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 37076542
- PMCID: PMC10115881
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37464-2
Disrupting the α-synuclein-ESCRT interaction with a peptide inhibitor mitigates neurodegeneration in preclinical models of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
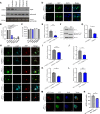
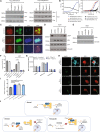
Accumulation of α-synuclein into toxic oligomers or fibrils is implicated in dopaminergic neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Here we performed a high-throughput, proteome-wide peptide screen to identify protein-protein interaction inhibitors that reduce α-synuclein oligomer levels and their associated cytotoxicity. We find that the most potent peptide inhibitor disrupts the direct interaction between the C-terminal region of α-synuclein and CHarged Multivesicular body Protein 2B (CHMP2B), a component of the Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport-III (ESCRT-III). We show that α-synuclein impedes endolysosomal activity via this interaction, thereby inhibiting its own degradation. Conversely, the peptide inhibitor restores endolysosomal function and thereby decreases α-synuclein levels in multiple models, including female and male human cells harboring disease-causing α-synuclein mutations. Furthermore, the peptide inhibitor protects dopaminergic neurons from α-synuclein-mediated degeneration in hermaphroditic C. elegans and preclinical Parkinson's disease models using female rats. Thus, the α-synuclein-CHMP2B interaction is a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
University of Toronto has submitted a patent application covering composition and use of the peptides, as well as the screening methods (US Patent 63/289,912, currently pending with PCT filed) with S.N., C.C.V., S.K.K., L.V.K., and P.M.K. as inventors. S.K.K., L.V.K., and P.M.K. have co-founded Synepark Therapeutics Inc to commercialize aspects of this research. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

