Development of Adenovirus-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidate in Indonesia
- PMID: 37076664
- PMCID: PMC10115376
- DOI: 10.1007/s12033-023-00749-4
Development of Adenovirus-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidate in Indonesia
Abstract
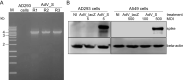
Covid-19 pandemic has struck worldwide by end of 2019 and the use of various vaccine platforms was one of the main strategies to end this. To meet the needs for vaccine technology equality among many countries, we developed adenovirus-based Covid-19 vaccine candidate in Indonesia. SARS-CoV-2 Spike gene (S) was constructed into pAdEasy vector. The recombinant serotype 5 Adenovirus (AdV_S) genome was transfected into AD293 cells to produce recombinant adenovirus. Characterization using PCR confirmed the presence of spike gene. Transgene expression analysis showed the expression of S protein in AdV_S infected AD293 and A549 cells. Optimization of viral production showed the highest titer was obtained at MOI of 0.1 and 1 at 4 days. The in vivo study was performed by injecting Balb/c mice with 3.5 × 107 ifu of purified adenovirus. The result showed that S1-specific IgG was increased up to 56 days after single-dose administration of AdV_S. Interestingly, significant increase of S1 glycoprotein-specific IFN-γ ELISpot was observed in AdV_S treated Balb/c mice. In conclusion, the AdV_S vaccine candidate was successfully produced at laboratory scale, immunogenic, and did not cause severe inflammation in Balb/c mice. This study serves as initial step towards manufacturing of adenovirus-based vaccine in Indonesia.
Keywords: AdV_S; Adenovirus; Covid-19; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccine; hAd5.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Statistik, B. P. (2021). 2020 Population Census. Berita Resmi Statistik No. 7/01/Th. XXIV. Retrieved April 26, 2022, from https://www.bps.go.id/pressrelease/2021/01/21/1854/hasil-sensus-penduduk...
-
- Voysey M, Clemens SAC, Madhi SA, Weckx LY, Folegatti PM, Aley PK, Angus B, Baillie VL, Barnabas SL, Bhorat QE, Bibi S, Briner C, Cicconi P, Collins AM, Colin-Jones R, Cutland CL, Darton TC, Dheda K, Zuidewind P. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. The Lancet. 2021;397(10269):99–111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sadoff J, Gray G, Vandebosch A, Cárdenas V, Shukarev G, Grinsztejn B, Goepfert PA, Truyers C, Fennema H, Spiessens B, Offergeld K, Scheper G, Taylor KL, Robb ML, Treanor J, Barouch DH, Stoddard J, Ryser MF, Marovich MA, ENSEMBLE Study Group Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against Covid-19. The New England journal of medicine. 2021 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2101544. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Halperin SA, Ye L, MacKinnon-Cameron D, Smith B, Cahn PE, Ruiz-Palacios GM, Ikram A, Lanas F, Lourdes Guerrero M, Muñoz Navarro SR, Sued O, Lioznov DA, Dzutseva V, Parveen G, Zhu F, Leppan L, Langley JM, Barreto L, Gou J, Zubkova T. Final efficacy analysis, interim safety analysis, and immunogenicity of a single dose of recombinant novel coronavirus vaccine (adenovirus type 5 vector) in adults 18 years and older: an international, multicentre, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-cont. The Lancet. 2022;399(10321):237–248. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02753-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Logunov DY, Dolzhikova IV, Shcheblyakov DV, Tukhvatulin AI, Zubkova OV, Dzharullaeva AS, Kovyrshina AV, Lubenets NL, Grousova DM, Erokhova AS, Botikov AG, Izhaeva FM, Popova O, Ozharovskaya TA, Esmagambetov IB, Favorskaya IA, Zrelkin DI, Voronina DV, Gintsburg AL. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: An interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. The Lancet. 2021;397(10275):671–681. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00234-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

