A redrawn map for the human motor cortex
- PMID: 37076716
- PMCID: PMC11824899
- DOI: 10.1038/d41586-023-01350-0
A redrawn map for the human motor cortex
Abstract
The human brain’s motor cortex is often regarded as a linear map with discrete sections, each controlling different parts of the body. The discovery that portions of the motor cortex have other functions points to a different type of map.
Keywords: Brain; Computational biology and bioinformatics; Neuroscience.
Figures
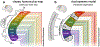
Comment on
-
A somato-cognitive action network alternates with effector regions in motor cortex.Nature. 2023 May;617(7960):351-359. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05964-2. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37076628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Penfield W & Boldrey E Brain 60, 389–443 (1937).
-
- Roux F-E, Niare M, Charni S, Giussani C & Durand J-B J. Physiol. (Lond.) 598, 5487–5504 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

