Delayed hypersensitivity reaction to cosmetic filler following two COVID-19 vaccinations and infection
- PMID: 37076880
- PMCID: PMC10115597
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-023-00788-1
Delayed hypersensitivity reaction to cosmetic filler following two COVID-19 vaccinations and infection
Abstract
Background: With ongoing COVID-19 vaccination schedules and the popularity of cosmetic fillers, it is important to examine and record associated adverse reactions to a more general audience of health care professionals. Case reports exist in subspecialty journals outlining reactions after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. This is one of the first cases published in Canada, and it highlights priorities and challenges faced by physicians in assessing and managing patients presenting with adverse reactions post vaccination.
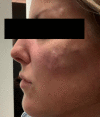
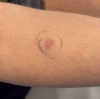
Case presentation: We present a case of a 43 -year-old women with delayed type 4 hypersensitivity reaction to hyaluronic acid cosmetic filler triggered by COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. We outline the clinical presentation, diagnosis, complications, and treatment of a late inflammatory reaction to hyaluronic acid filler and highlight the treatment priorities for clinicians faced with similar presentations.
Conclusion: The differential diagnosis of delayed onset nodules formation post filler injection is broad and includes redistribution of fillers, inflammatory reaction to biofilm, and delayed hypersensitivity reaction. As result, in order to make the right diagnosis, administer the appropriate treatment and achieve great cosmetic results, we highly recommend seeking expert opinion from dermatologist, plastic surgeon and allergist immunologist in a timely manner.
Keywords: COVID vaccine; Cosmetic filler; Delayed hypersensitivity reactions; Hyaluronic acid injection.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyaluronic acid soft tissue filler delayed inflammatory reaction following COVID-19 vaccination - A case report.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021 Sep;20(9):2684-2690. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14312. Epub 2021 Jul 1. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34174156 Free PMC article.
-
First reported case of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to non-hyaluronic acid Polycaprolactone dermal filler following COVID-19 vaccination: A case report and a review of the literature.Clin Case Rep. 2022 Feb 6;10(2):e05343. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.5343. eCollection 2022 Feb. Clin Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35145687 Free PMC article.
-
Hypersensitivity reaction to hyaluronic acid dermal filler after the Pfizer vaccination against SARS-CoV-2.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Dec;113:233-235. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.09.066. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34597761 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse reactions to cosmetic implants after COVID-19 vaccination: A literature review.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Dec;22(12):3199-3212. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15828. Epub 2023 Aug 17. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37592436 Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Literature of Delayed Inflammatory Reactions After Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection to Estimate the Incidence of Delayed Type Hypersensitivity Reaction.Aesthet Surg J. 2020 Apr 14;40(5):NP286-NP300. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjz222. Aesthet Surg J. 2020. PMID: 31410442
Cited by
-
A Structured Approach for Treating Calcium Hydroxylapatite Focal Accumulations.Aesthet Surg J. 2024 Jul 15;44(8):869-879. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjae031. Aesthet Surg J. 2024. PMID: 38366791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Late-Onset Reactions after Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Consensus Recommendation on Etiology, Prevention and Management.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Jul;14(7):1767-1785. doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01202-3. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38907876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination or Infection on the Safety and Efficacy of Aesthetic Injections: A Systematic Review.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Jun;48(12):2343-2352. doi: 10.1007/s00266-023-03769-2. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38302710
References
-
- Micheels P. Human anti-hyaluronic acid antibodies: is it possible? Dermatol Surg. 2001 Feb;27(2):185 – 91. 10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00248.x. PMID: 11207696. Accessed 3rd September 2022 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous