Novel predictors of immune checkpoint inhibitor response and prognosis in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with bone metastasis
- PMID: 37076988
- PMCID: PMC10278505
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5952
Novel predictors of immune checkpoint inhibitor response and prognosis in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with bone metastasis
Abstract
Backgrounds: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) can significantly prolong the survival of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, few studies on the therapeutic effects of ICIs on bone metastases were performed.
Methods: This retrospective study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of ICIs and determine predictors of favorable ICI response and prognosis in 55 advanced NSCLC patients with bone metastases who initiated ICI treatment between 2016 and 2019, with a mean follow-up period of 23.2 months. Patients were classified into responders (complete or partial response) and non-responders (stable or progressive disease) according to the MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDA) criteria, and the predictors of therapeutic response were identified using multivariate logistic regression analysis. Furthermore, overall survival from the time of ICI administration to the final follow-up or death was evaluated, and prognostic predictors were identified using Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.
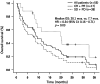
Results: ICI response rate was 30.9% (complete in three cases, partial in 14). Median survival time was 9.3 months, with 1-year and 2-year survival rates of 40.6% and 19.3%, respectively. Responders survived significantly longer than non-responders (p = 0.03). Based on the receiver operating characteristic curve, the predictive cutoff value of the pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) was 2.1. Multivariate analysis identified female sex (p = 0.03), use of ICIs as first-line therapy (p < 0.01), and NLR <2.1 (p = 0.03) as significant predictors of therapeutic response, whereas concomitant use of a bone-modifying agent (p < 0.01), Katagiri score ≤6 points (p < 0.01), and NLR <2.1 (p = 0.02) were identified as significant predictors of good prognosis.
Conclusions: This study identified some novel predictors for favorable therapeutic response and prognosis in advanced NSCLC patients with bone metastases undergoing ICI treatment. Pretreatment NLR less than 2.1 can be considered the most important predictor.
Keywords: bone metastasis; denosumab; immune checkpoint inhibitor; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; non-small-cell lung cancer.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors With or Without Bone-Targeted Therapy in NSCLC Patients With Bone Metastases and Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 10;12:697298. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.697298. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858389 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors and denosumab improves clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer with bone metastases.Lung Cancer. 2024 Jul;193:107858. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2024.107858. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Lung Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38901176
-
Factors related to rapid progression of non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese patients treated using single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment.Thorac Cancer. 2020 May;11(5):1170-1179. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13370. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32134200 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes of non-small cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastases after immune checkpoint inhibitor treatments.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Jun;150:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.03.037. Epub 2021 Apr 18. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33882375
-
Predictive value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Aug;85:106677. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106677. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32531712
Cited by
-
Circulating Natural Killer Cells as Prognostic Value for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Correlation with Sarcopenia.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 12;15(14):3592. doi: 10.3390/cancers15143592. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509255 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with immunotherapy efficacy in patients with advanced cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):446. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84890-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747391 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors in patients with bone metastasis of lung cancer after immune checkpoint inhibitors: A retrospective study.World J Orthop. 2024 Dec 18;15(12):1155-1163. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i12.1155. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39744733 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect between denosumab and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI)? A retrospective study of 268 patients with ICI and bone metastases.J Bone Oncol. 2024 Sep 21;48:100634. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2024.100634. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Bone Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39381634 Free PMC article.
-
Response rate specific to bone metastasis of various cancers for immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024 Aug;34(6):2823-2833. doi: 10.1007/s00590-024-04018-1. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 38836904
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Zhang N, Jiang J, Tang S, Sun G. Predictive value of neutrophil‐lymphocyte ratio and platelet‐lymphocyte ratio in non‐small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a meta‐analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106677. - PubMed
-
- Moro‐Sibilot D, Smit E, de Castro Carpeno J, et al. Outcomes and resource use of non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with first‐line platinum‐based chemotherapy across Europe: FRAME prospective observational study. Lung Cancer. 2015;88:215‐222. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7‐34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical