Clinical effectiveness of medical ozone therapy in COVID-19: the evidence and gaps map
- PMID: 37077114
- PMCID: PMC10226688
- DOI: 10.4103/2045-9912.372819
Clinical effectiveness of medical ozone therapy in COVID-19: the evidence and gaps map
Abstract
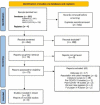
Ozone therapy (OT), a medical procedure, has been showing good results during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19). We aimed to build an evidence and gaps map (EGM) of OT in the COVID-19 ranking the articles found according to levels of evidence and outcomes. The EGM brings bubbles of different sizes and different colors according to the articles. The OT intervention used was major or minor autohemotherapy, rectal insufflation and ozonized saline solution. EGM was based on 13 clinical studies using OT for COVID-19 involving a total of 271 patients. We found 30 outcomes related to OT in COVID-19. Our EGM divided the outcomes into six groups: 1-clinical improvement; 2-hospitalization; 3-inflammatory, thromboembolic, infectious, or metabolic markers; 4-radiological aspects, 5-viral infection and 6-adverse events. Major autohemotherapy was present in 19 outcomes, followed by rectal insufflation. Improvement in clinical symptoms of COVID-19, improvement of respiratory function, improvement of oxygen saturation, reduction in hospital internment, decrease in C-reactive protein, decrease in ferritin, decrease in lactate dehydrogenase, decrease in interleukin 6, decrease in D-dimer, radiological improvement of lung lesions and absence of reported adverse events were related in the papers. The most commonly used concentrations of OT in major autohemotherapy and in rectal insufflation were 40 μg/mL and 35 μg/mL, respectively. Here, we bring the first EGM showing the efficacy and safety of OT in the treatment of COVID-19. OT can be used as integrative medical therapy in COVID-19 at a low cost and improve the health conditions of the patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-COV-2; complementary therapies; coronavirus; evidence and gaps map; evidence map; medical ozone therapy; medicinal ozone; ozone; ozone therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of ozone therapy in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review.Med Gas Res. 2023 Oct-Dec;13(4):165-171. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.369237. Med Gas Res. 2023. PMID: 37077113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and efficacy of ozone therapy in mild to moderate COVID-19 patients: A phase 1/11 randomized control trial (SEOT study).Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Feb;91:107301. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107301. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33421928 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Potential therapeutic effect of oxygen-ozone in controlling of COVID-19 disease.Med Gas Res. 2022 Apr-Jun;12(2):33-40. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.325989. Med Gas Res. 2022. PMID: 34677149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ozone therapy for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: Preliminary report of a prospective case-control study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jan;90:107261. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107261. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33310665 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Blood ozonization in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 pneumonia: a single centre experience.Intern Emerg Med. 2021 Apr;16(3):669-675. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02542-6. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Intern Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33131033 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of ozone therapy in dentistry with approach of healing, pain management, and therapeutic outcomes: a systematic review of clinical trials.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Mar 26;25(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05790-0. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40140788 Free PMC article.
-
Modifications of Blood Molecular Components after Treatment with Low Ozone Concentrations.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 6;24(24):17175. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417175. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139004 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and socio-environmental factors in the transmission of COVID-19: a comprehensive analysis of epidemiology and mechanisms.BMC Public Health. 2024 Aug 13;24(1):2196. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19749-3. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39138466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in an Experimental Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Model in Rats: The Role of Ozone Therapy and Trimetazidine.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 25;14(9):1051. doi: 10.3390/biom14091051. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334818 Free PMC article.
-
Ozone-Oxygen Therapy to Prevent HPV-Related Cancers of the Lower Gynecological Tract in Infected Patients: The Rationale for Further Developments.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;17(3):543. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030543. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bocci V, Di Paolo N. Oxygen-ozone therapy in medicine: an update. Blood Purif. 2009;28:373–376. - PubMed
-
- Viebahn-Hänsler R, León Fernández OS, Fahmy Z. Ozone in medicine: the low-dose ozone concept—guidelines and treatment strategies. Ozone Sci Eng. 2012;34:408–424.
-
- Mishra SK, Pramanik R, Das P, et al. Role of intra-articular ozone in osteo-arthritis of knee for functional and symptomatic improvement. Ind J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;22:65–69.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

