Development of a new cellular immunological detection method for tuberculosis based on HupB protein induced IL-6 release test
- PMID: 37077246
- PMCID: PMC10106748
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1148503
Development of a new cellular immunological detection method for tuberculosis based on HupB protein induced IL-6 release test
Abstract
Objective: As a virulence factor, HupB plays important roles in the survival of MTB after infection and modulates the host immune response. In the current study, we aim to explore a new cellular immunological detection method for tuberculosis infection detection based on HupB protein.
Methods: HupB was used to stimulate PBMCs extracted from pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) patients, and secreted cytokines was examined. Then, we constructed a single center and a multi-center clinical trials to collect PBMCs from PTB patients, nPTB patients, or healthy volunteers to verify our findings.
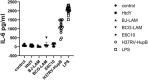
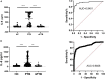
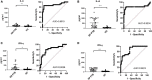
Results: Cytokine's screening illustrated that IL-6 was the only cytokine released after HupB stimulation. Single-center and multi-center clinical trials showed that HupB stimulation significantly increased the level of IL-6 in the supernatant of PBMCs from PTB patients. Then we compared the specificity and sensitivity of HupB induced IL-6 release assay with ESAT-6 and CFP10 induced interferon γ release assay (IGRA), and found in smear positive PTB patients, the specificity and sensitivity of HupB induced IL-6 release assay was better than IGRA, and in smear negative PTB patients, the sensitivity was better. Combination of both assays provided an improved specificity and sensitivity for tuberculosis diagnosis.
Conclusion: This study explored an immunological detection method for tuberculosis infection cells based on HupB protein-induced IL-6 release test, which can be used to enhance the diagnosis diagnostic accuracy of TB.
Keywords: HupB; IGRA; IL-6; PBMCs; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023 Yu, Jiang, Li, Zhou, Wei, Li, Zhang, Hu, Wu, Wang, Wu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Th2 immune response by the iron-regulated protein HupB of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Indian J Tuberc. 2022 Jan;69(1):90-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2021.04.011. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Indian J Tuberc. 2022. PMID: 35074158
-
Whole blood interferon-γ release assay is insufficient for the diagnosis of sputum smear negative pulmonary tuberculosis.Yonsei Med J. 2014 May;55(3):725-31. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.725. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Yonsei Med J. 2014. PMID: 24719140 Free PMC article.
-
Significant difference in Th1/Th2 paradigm induced by tuberculosis-specific antigens between IGRA-positive and IGRA-negative patients.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 31;13:904308. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.904308. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119060 Free PMC article.
-
[Evolution of IGRA researches].Kekkaku. 2008 Sep;83(9):641-52. Kekkaku. 2008. PMID: 18979999 Review. Japanese.
-
[Characteristics of a diagnostic method for tuberculosis infection based on whole blood interferon-gamma assay].Kekkaku. 2006 Nov;81(11):681-6. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17154047 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Garbers C., Heink S., Korn T., Rose-John S. (2018). Interleukin-6: Designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17 395–412. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

