Synthesis and characterization of low surface energy thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers based on polydimethylsiloxane
- PMID: 37077257
- PMCID: PMC10108671
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra01142a
Synthesis and characterization of low surface energy thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers based on polydimethylsiloxane
Abstract
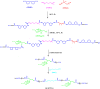
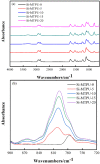
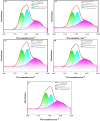
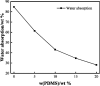
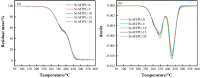
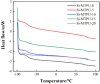
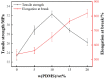
Organosilicon modified polyurethane elastomers (Si-MTPUs) were synthesized in order to improve the anti-graffiti property of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers (TPUs). Si-MTPUs were prepared from polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and polytetramethylene glycol (PTMG) as mixed soft segment, 1,4-butanediol (BDO) and imidazole salt ionic liquid N-glyceryl-N-methyl imidazolium chloride ([MIMl,g]Cl) used as chain extender, and 4,4'-dicyclohexylmethane diisocyanate (HMDI). The structure, thermal stability, mechanical properties and physical crosslinking density of Si-MTPUs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetry analysis (TGA), mechanical test and low field nuclear magnetic resonance. Surface energy and water absorption were characterized by static contact angle test and water resistance test, and anti-graffiti and self-cleaning properties were characterized with water, milk, ink, lipstick, oily markers and spray paint. It was found that the mechanical properties of Si-MTPU-10 with the content of PDMS 10 wt% were optimized, with a maximum tensile strength of 32.3 MPa and elongation at break of 656%. Surface energy reached the minimum value of 23.1 mN m-1 with the best anti-graffiti performance, which no longer decreased with the increase of PDMS contents. This work provides novel idea and strategy for the preparation of low surface energy TPUs.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Green Approach to the Synthesis of Bio-Based Thermoplastic Polyurethane Elastomers with Partially Bio-Based Hard Blocks.Materials (Basel). 2021 Apr 30;14(9):2334. doi: 10.3390/ma14092334. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946420 Free PMC article.
-
Polysiloxane-Based Polyurethanes with High Strength and Recyclability.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 20;23(20):12613. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012613. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293466 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning Thermal, Morphological, and Physicochemical Properties of Thermoplastic Polyurethanes (TPUs) by the 1,4-Butanediol (BDO)/Dipropylene Glycol (DPG) Ratio.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Aug 3;14(15):3164. doi: 10.3390/polym14153164. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35956679 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Elastomers by Restriction of Crystallization of Soft Segment.Materials (Basel). 2010 Dec 1;3(12):5097-5110. doi: 10.3390/ma3125097. Materials (Basel). 2010. PMID: 28883371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of soft segment structure, hydrogen bonding, and diisocyanate symmetry on morphology and properties of segmented thermoplastic polyurethanes and polyureas.Turk J Chem. 2023 Jun 22;47(5):1007-1017. doi: 10.55730/1300-0527.3591. eCollection 2023. Turk J Chem. 2023. PMID: 38173740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khalifa M. Anandhan S. Wuzella G. Lammer H. Mahendran A. R. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020;59:1751–1769.
-
- Atiqah A. Mastura M. T. Ali B. A. A. Jawaid M. Sapuan S. M. Curr. Org. Synth. 2017;14:233–248.
-
- Cheng B. X. Gao W. C. Ren X. M. Ouyang X. Y. Zhao Y. Zhao H. Wu W. Huang C. X. Liu Y. Liu X. Y. Li H. N. Li R. K. Y. Polym. Test. 2022;107:107489.
-
- Xu J. Wang X. Y. Ruan H. W. Zhang X. R. Zhang Y. M. Yang Z. H. Wang Q. H. Wang T. M. Polym. Chem. 2022;13:2420–2441.
-
- Tian S. Q. Polymers. 2020;12:1996. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

