Role of apigenin in high glucose-induced retinal microvascular endothelial cell dysfunction via regulating NOX4/p38 MAPK pathway in vitro
- PMID: 37077488
- PMCID: PMC10089914
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2023.04.04
Role of apigenin in high glucose-induced retinal microvascular endothelial cell dysfunction via regulating NOX4/p38 MAPK pathway in vitro
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the retinoprotective role of Apigenin (Api) against high glucose (HG)-induced human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMECs), and to explore its regulatory mechanism.
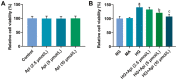
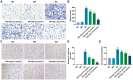
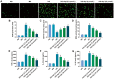
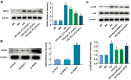
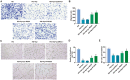
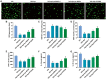
Methods: HRMECs were stimulated by HG for 48h to establish the in vitro cell model. Different concentrations of Api (2.5, 5, and 10 µmol/L) were applied for treatment. Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), Transwell, and tube formation assays were performed to examine the effects of Api on the viability, migration, and angiogenesis in HG-induced HRMECs. Vascular permeability was evaluated by Evans blue dye. The inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress-related factors were measured using their commercial kits. Protein expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase 4 (NOX4) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) was measured by Western blot.
Results: Api prevented HG-induced HRMECs viability, migration, angiogenesis, and vascular permeability in a concentration-dependent manner. Meanwhile, Api also concentration-dependently inhibited inflammation and oxidative stress in HRMECs exposed to HG. In addition, HG caused an elevated expression of NOX4, which was retarded by Api treatment. HG stimulation facilitated the activation of p38 MAPK signaling in HRMECs, and Api could weaken this activation partly via downregulating NOX4 expression. Furthermore, overexpression of NOX4 or activation of p38 MAPK signaling greatly weakened the protective role of Api against HG-stimulated HRMECs.
Conclusion: Api might exert a beneficial role in HG-stimulated HRMECs through regulating NOX4/p38 MAPK pathway.
Keywords: NOX4; apigenin; glucose; p38 MAPK; retinal microvascular endothelial cell.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genipin relieves diabetic retinopathy by down-regulation of advanced glycation end products via the mitochondrial metabolism related signaling pathway.World J Diabetes. 2023 Sep 15;14(9):1349-1368. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i9.1349. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37771331 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium butyrate inhibits activation of ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway and angiogenesis in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 18;45(1):108. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03458-w. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40100328
-
[Wogonoside alleviates high glucose-induced dysfunction of retinal microvascular endothelial cells and diabetic retinopathy in rats by up-regulating SIRT1].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Apr 20;42(4):463-472. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.04.02. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35527482 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
MiR-124-3p Suppresses the Dysfunction of High Glucose-Stimulated Endothelial Cells by Targeting G3BP2.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 8;12:723625. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.723625. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34691148 Free PMC article.
-
Fenofibrate mitigates the dysfunction of high glucose-driven human retinal microvascular endothelial cells by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome.Int J Ophthalmol. 2025 May 18;18(5):792-801. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2025.05.04. eCollection 2025. Int J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40385128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong TY, Cheung CMG, Larsen M, Sharma S, Simó R. Diabetic retinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16012. - PubMed
-
- Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271–281. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
