Locked nucleic acid real-time polymerase chain reaction method identifying two polymorphisms of hepatitis B virus genotype C2 infections, rt269L and rt269I
- PMID: 37077521
- PMCID: PMC10107212
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1721
Locked nucleic acid real-time polymerase chain reaction method identifying two polymorphisms of hepatitis B virus genotype C2 infections, rt269L and rt269I
Abstract
Background: The presence of two distinct hepatitis B virus (HBV) Pol RT polymorphisms, rt269L and rt269I, could contribute to the unique clinical or virological phenotype of HBV genotype C2. Therefore, a simple and sensitive method capable of identifying both types in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients infected with genotype C2 should be developed.
Aim: To develop a novel simple and sensitive locked nucleic acid (LNA)-real time-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method capable of identifying two rt269 types in CHB genotype C2 patients.
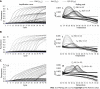
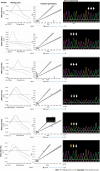
Methods: We designed proper primer and probe sets for LNA-RT-PCR for the separation of rt269 types. Using synthesized DNAs of the wild type and variant forms, melting temperature analysis, detection sensitivity, and endpoint genotyping for LNA-RT-PCR were performed. The developed LNA-RT-PCR method was applied to a total of 94 CHB patients of genotype C2 for the identification of two rt269 polymorphisms, and these results were compared with those obtained by a direct sequencing protocol.
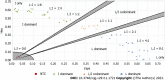
Results: The LNA-RT-PCR method could identify two rt269L and rt269I polymorphisms of three genotypes, two rt269L types ['L1' (WT) and 'L2'] and one rt269I type ('I') in single (63 samples, 72.4%) or mixed forms (24 samples, 27.6%) in 87 (92.6% sensitivity) of 94 samples from Korean CHB patients. When the results were compared with those obtained by the direct sequencing protocol, the LNA-RT-PCR method showed the same results in all but one of 87 positive detected samples (98.9% specificity).
Conclusion: The newly developed LNA-RT-PCR method could identify two rt269 polymorphisms, rt269L and rt269I, in CHB patients with genotype C2 infections. This method could be effectively used for the understanding of disease progression in genotype C2 endemic areas.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; Genotype C2; Hepatitis B virus; Locked nucleic acid-real time-polymerase chain reaction; Polymerase; rt269.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Nannini P, Sokal EM. Hepatitis B: changing epidemiology and interventions. Arch Dis Child. 2017;102:676–680. - PubMed
-
- Abara WE, Qaseem A, Schillie S, McMahon BJ, Harris AM High Value Care Task Force of the American College of Physicians and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Abraham GM, Centor R, DeLong DM, Gantzer HE, Horwitch CA, Humphrey LL, Jokela JA, Li JMW, Lohr RH, López AM, McLean RM. Hepatitis B Vaccination, Screening, and Linkage to Care: Best Practice Advice From the American College of Physicians and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167:794–804. - PubMed
-
- Yuen MF, Chen DS, Dusheiko GM, Janssen HLA, Lau DTY, Locarnini SA, Peters MG, Lai CL. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18035. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

