Global research trends on COVID-19 and stroke: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 37077570
- PMCID: PMC10106632
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1147867
Global research trends on COVID-19 and stroke: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: The pandemic of COVID-19 has had a profound influence on worldwide healthcare systems. Our study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis to explore the impact of COVID-19 on stroke and to highlight the major research trends in this field.
Methods: We searched the original articles and review articles regarding COVID-19 and stroke from the Web of Science collection (WOSCC) database between January 1, 2020 and December 30, 2022. Subsequently, we performed bibliometric analyses and visualization using VOSviewer, Citespace, and Scimago Graphica.
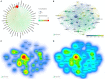
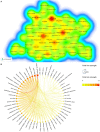
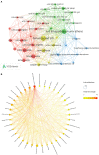
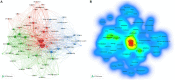
Results: A total of 608 original articles or review articles were included. JOURNAL OF STROKE and CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES published the most studies on this subject (n = 76), while STROKE was the source of the most-cited references (n = 2,393). The United States is the most influential country in this field, with the highest number of publications (n = 223) and citations (n = 5,042). Shadi Yaghi from New York University is the most prolific author in the field, while Harvard Medical School is the most prolific institution. In addition, through keyword analysis and reference co-citation analysis, three major research topics were identified: (i) the impact of COVID-19 on stroke outcomes (including risk factors, clinical characteristics, mortality, stress, depression, comorbidities, etc.); (ii) the management and care of stroke patients during the COVID-19 pandemic (including thrombolysis, thrombectomy, telemedicine, anticoagulation, vaccination, etc.); and (iii) the potential relationship and pathological mechanism between COVID-19 and stroke (including renin-angiotensin system activation, SARS-CoV-2 virus-induced inflammation leading to endothelial impairment, coagulopathy, etc.).
Conclusion: Our bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on COVID-19 and stroke and highlights key areas of focus in the field. Optimizing the treatment of COVID-19-infected stroke patients and elucidating the underlying pathogenic mechanisms of COVID-19 and stroke co-morbidity are key areas of future research that will be beneficial in improving the prognosis of stroke patients during the ongoing COVID-19 epidemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Citespace; VOSviewer; Web of Science; bibliometric analysis; research hotspots; stroke; visual analysis.
Copyright © 2023 Zeng, Cao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of post-stroke aphasia rehabilitation: a bibliometric study and visualization analysis.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 May 11;17:1176923. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1176923. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37250700 Free PMC article.
-
Scars of COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis of post-COVID-19 fibrosis.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 20;10:967829. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.967829. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36203683 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Structure and Emerging Trends of Telerehabilitation in Recent 20 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 20;10:904855. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.904855. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35795695 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and trends of post-stroke depression rehabilitation: a bibliometric analysis from 2003 to 2024.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 4;16:1526506. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1526506. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40255888 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and trends in healthcare workers' resilience: A bibliometric and visualized analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 24;10(15):e35107. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35107. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170181 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A bibliometric analysis of research trends and hotspots of pilocytic astrocytoma from 2004 to 2023.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Dec 26;48(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-03139-9. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 39724457 Free PMC article.
-
Post-COVID depression and anxiety are multicausal and not necessarily due to SARS-CoV-2 infection.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025 Jun;275(4):1263-1264. doi: 10.1007/s00406-024-01800-4. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 38829442 No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

