Teneligliptin, a DPP-4 Inhibitor, Improves Vascular Endothelial Function via Divergent Actions Including Changes in Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells
- PMID: 37077576
- PMCID: PMC10108873
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S403125
Teneligliptin, a DPP-4 Inhibitor, Improves Vascular Endothelial Function via Divergent Actions Including Changes in Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells
Abstract
Purpose: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors increase endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in peripheral blood circulation. However, the underlying mechanisms and effects on vascular endothelial function remain unclear. We evaluated whether the DPP-4 inhibitor teneligliptin increases circulating EPCs by inhibiting stromal-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) and improves flow-mediated vascular dilatation (FMD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or its risk factors.
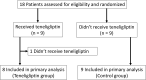
Patients and methods: This single-center, open-label, prospective, randomized controlled trial evaluated 17 patients (hemoglobin A1c ≤7.5% and peak creatinine phosphokinase <2000 IU/mL) with ACS or a history of ACS or multiple cardiovascular risk factors. Metabolic variables of glucose and lipids, circulating EPCs, plasma DPP-4 activity, and SDF-1α levels, and FMD were evaluated at baseline and 28 ± 4 weeks after enrollment. Patients were randomly assigned to either the teneligliptin (n = 8) or control (n = 9) groups.
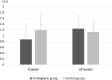
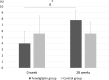
Results: The DPP-4 activity (∆-509.5 ± 105.7 vs ∆32.8 ± 53.4 μU/mL) and SDF-1α levels (∆-695.6 ± 443.2 vs ∆11.1 ± 193.7 pg/mL) were significantly decreased after 28 weeks in the teneligliptin group than those in the control group. The number of EPCs showed an increasing trend in the teneligliptin treated group; albeit this did not reach statistical significance. Glucose and lipid levels were not significantly different between the groups before and after 28 weeks. However, FMD was significantly improved in the teneligliptin group when compared to the control group (∆3.8% ± 2.1% vs ∆-0.3% ± 2.9%, P=0.006).
Conclusion: Teneligliptin improved FMD through a mechanism other than increasing the number of circulating EPCs.
Keywords: DPP-4 inhibitor; endothelial progenitor cell; flow-mediated dilation; teneligliptin; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2023 Akashi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Naoyuki Akashi reports grants from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, during the conduct of the study. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Sitagliptin on the Coronary Flow Reserve, Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Stromal Cell-derived Factor-1alpha.Intern Med. 2019 Oct 1;58(19):2773-2781. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2616-19. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 31243210 Free PMC article.
-
Vildagliptin, but not glibenclamide, increases circulating endothelial progenitor cell number: a 12-month randomized controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Feb 23;16(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0503-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28231835 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Active Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1α and Endothelial Progenitor Cells are Equally Increased by Alogliptin in Good and Poor Diabetes Control.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2017 Nov 27;10:1179551417743980. doi: 10.1177/1179551417743980. eCollection 2017. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 29225483 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Teneligliptin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2018 May 4;9:449. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00449. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29780322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Teneligliptin : expectations for its pleiotropic action.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015 Feb;16(3):417-26. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2015.1000301. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25597385 Review.
Cited by
-
A case report of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor-related kidney disease combined with renal cancer.Front Nephrol. 2024 Jul 29;4:1409098. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2024.1409098. eCollection 2024. Front Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39135967 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibition on the endothelial control of the vascular tone.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 Oct 1;325(4):C972-C980. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00246.2023. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37642237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Teneligliptin mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.World J Diabetes. 2024 Apr 15;15(4):724-734. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.724. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38680706 Free PMC article.
-
Teneligliptin mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy through inflammasome inhibition: Insights from experimental studies.World J Diabetes. 2024 Dec 15;15(12):2370-2375. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i12.2370. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39676805 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of DPP-4 inhibitors on cardiovascular disease treatment: a comprehensive review of current therapeutic strategies and future directions.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Apr 17;52(1):400. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10458-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40244362 Review.
References
-
- Davies MJ, D’Alessio DA, Fradkin J, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2018;61(12):2461–2498. doi:10.1007/s00125-018-4729-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

