miR-31-5p as a Potential Circulating Biomarker and Tracer of Clinical Improvement for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
- PMID: 37077658
- PMCID: PMC10110370
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/2305163
miR-31-5p as a Potential Circulating Biomarker and Tracer of Clinical Improvement for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs are endogenous, small noncoding RNA molecules that play a pivotal role in the regulation of gene expression. MicroRNAs are involved in many biological processes such as proliferation, cell differentiation, neovascularization, and apoptosis. Studies on microRNA expression may contribute to a better understanding of the pathomechanism of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) and consequently enable the development of new therapeutic measures using antisense miRNAs (antagomirs). In this study, we evaluated the level of miR-31-5p in the serum of patients with CIDP and its correlation with the miR-31-5p level and clinical presentation and electrophysiological and biochemical parameters.
Methods: The study group consisted of 48 patients, mean age 61.60 ± 11.76, who fulfilled the diagnostic criteria of a typical variant of CIDP. The expression of miR-31-5p in patient serum probes was investigated by droplet digital PCR. The results were correlated with neurophysiological findings and the patient's clinical and biochemical parameters.
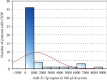
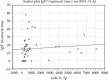
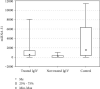
Results: The mean copy number of miRNA-31 in 100 μl serum was 1288.64 ± 2001.02 in the CIDP group of patients, while in the control group, it was 3743.09 ± 4026.90. There was a significant positive correlation (0.426) between IgIV treatment duration and miR-31-5p expression. Patients without IgIV treatment showed significantly lower levels of miR-31 compared to the treated group (259.44 ± 304.02 vs. 1559.48 ± 2168.45; p = 0.002). The group of patients with body weight > 80 kg showed statistically significantly lower levels of miRNA-31-5p than the patients with lower body weight (934.37 ± 1739.66 vs. 1784.62 ± 2271.62, respectively; p = 0.014). Similarly, the patients with elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein levels had significantly higher miRNA-31-5p expression than those with normal protein levels (1393.93 ± 1932.27 vs. 987.38 ± 2364.10, respectively; p = 0.044).
Conclusion: The results may support the hypothesis that miR-31-5p is strongly involved in the autoimmune process in CIDP. The positive correlation between higher miR-31-5p levels and duration of IVIg treatment may be an additional factor explaining the efficacy of prolonged IVIg therapy in CIDP.
Copyright © 2023 Edyta Dziadkowiak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disease activity in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: association between circulating B-cell subsets, cytokine levels, and clinical outcomes.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Jan 9;215(1):65-78. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad103. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37638717 Free PMC article.
-
Motor unit number index (MUNIX) in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: A potential role in monitoring response to intravenous immunoglobulins.Clin Neurophysiol. 2019 Oct;130(10):1743-1749. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.06.231. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31400577
-
Genetic biomarkers for intravenous immunoglobulin response in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy.Eur J Neurol. 2021 May;28(5):1677-1683. doi: 10.1111/ene.14742. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33460483 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, a time to start and a time to stop.J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2016 Sep;21(3):121-7. doi: 10.1111/jns.12176. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2016. PMID: 27241239 Review.
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP): mechanisms of action and clinical and genetic considerations.Expert Rev Neurother. 2022 Nov-Dec;22(11-12):953-962. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2022.2169134. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Expert Rev Neurother. 2022. PMID: 36645654 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-31-5p regulates the neuroinflammatory response via TRAF6 in neuropathic pain.Biol Direct. 2024 Jan 24;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00434-1. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 38267979 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis-A Key to Understanding and Managing Disease Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 11;25(16):8751. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168751. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Biomarker Strategies in Autoimmune Neuromuscular Diseases.Cells. 2023 Oct 15;12(20):2456. doi: 10.3390/cells12202456. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An electrochemical biosensor for the detection of microRNA-31 as a potential oral cancer biomarker.J Biol Eng. 2025 Mar 25;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13036-025-00492-1. J Biol Eng. 2025. PMID: 40133958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao G., Han C., Zhang Z., Wang L., Xu J. Increased expression of microRNA-31-5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via regulating Sp1 transcription factor in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. . 2017;490(2):371–377. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.050. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

