Case Report: Coexistence of bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: Therapeutic challenge and IL17A-targeted parallel treatment strategy
- PMID: 37077669
- PMCID: PMC10108845
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1148660
Case Report: Coexistence of bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: Therapeutic challenge and IL17A-targeted parallel treatment strategy
Abstract
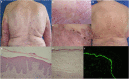
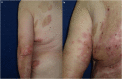
Autoimmune blistering diseases of the skin have all been reported in patients with psoriasis, bullous pemphigoid (BP) being the most frequently observed. The pathophysiologic triggers for BP in psoriatic patients are unclear. Recent observational studies have suggested that chronic psoriatic inflammation may cause pathological changes to the basement membrane zone, thus inducing autoimmunity against BP antigens through cross reactivity and "epitope spreading." The coexistence of BP and psoriasis poses challenging therapeutic dilemmas related to the incompatibility of their standard treatments. Considering the probable common immunologic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of these inflammatory skin disorders, a suitable treatment regimen should be applied for their parallel control. We report three patients, who developed BP in the course of preceding long-lasting psoriasis. Secukinumab was administered as first-line treatment with promising therapeutic effect for both skin disorders and long-term disease control in two of the cases. In the third case, parallel disease control was initially achieved with methotrexate. A few years later, secukinumab was used for the treatment of a relapse of both dermatoses but worsening of BP was observed and methotrexate was reintroduced. Our experience on the therapeutic potential of secukinumab in BP is supported by the data in the literature. Recently, it was demonstrated that the proinflammatory cytokine IL17A has a functional role in the process of skin inflammation in BP, similarly to psoriasis. IL17A inhibition has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy in patients with extensive or refractory BP but paradoxical development of BP after secukinumab treatment for psoriasis has also been described. This controversy emphasizes the need for further investigation into the development of optimal treatment strategies and recommendations.
Keywords: IL17A; biologics; bullous pemphigoid; psoriasis; secukinumab; treatment strategies.
Copyright © 2023 Drenovska, Valeva, Shahid and Vassileva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful secukinumab treatment of active bullous pemphigoid and chronic severe psoriasis: a case report.Australas J Dermatol. 2022 May;63(2):e155-e158. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13803. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Australas J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35138643
-
The Intriguing Links between Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 31;12(1):328. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010328. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36615129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Coexisting Bullous Pemphigoid and Psoriasis: A Review.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022 Nov;23(6):869-879. doi: 10.1007/s40257-022-00719-7. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35964277 Review.
-
Association between bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies.Australas J Dermatol. 2019 Feb;60(1):23-28. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12899. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Australas J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30141189
-
Successful Treatment of Psoriasis Combined with Bullous Pemphigoid with Dupilumab: A Case Report.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Jun 20;16:1583-1587. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S415019. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37359718 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Management of a Case of Severe Psoriasis Coexistent with Bullous Pemphigoid in the Elderly.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2023 Aug 22;13:27-31. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S417427. eCollection 2023. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2023. PMID: 37635856 Free PMC article.
-
Bullous Pemphigoid Overlapping Psoriasis Vulgaris: A Rare Case Report and Literature Review.Clin Pract. 2025 May 8;15(5):91. doi: 10.3390/clinpract15050091. Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 40422272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of the role of interleukin-17 inhibitors in bullous pemphigoid: therapeutic and paradoxical effects.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Mar 11;317(1):544. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-04052-x. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 40067544
-
Bullous pemphigoid burden of disease, management and unmet therapeutic needs.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025 Feb;39(2):290-300. doi: 10.1111/jdv.20313. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025. PMID: 39297242 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pietrzak A, Bartosińska J, Chodorowska G, Szepietowski J, Paluszkiewicz P, Schwartz R. Cardiovascular aspects of psoriasis vulgaris. Int J Dermatol. (2013) 52:153–62. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Nguyen T, Poon K, Herrinton L. The association of psoriasis with autoimmune diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2012) 67:924–30. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

