The influence of curcumin additives on the viability of probiotic bacteria, antibacterial activity against pathogenic microorganisms, and quality indicators of low-fat yogurt
- PMID: 37077903
- PMCID: PMC10106739
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1118752
The influence of curcumin additives on the viability of probiotic bacteria, antibacterial activity against pathogenic microorganisms, and quality indicators of low-fat yogurt
Abstract
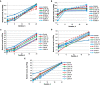
Curcumin is a nutraceutical with unique anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and antimicrobial properties. In this study, we aimed to examine the advantages of the use of water dispersible and highly bioavailable form of standardized turmeric extract (Curcuma longa L.)-NOMICU® L-100 (N) in the formulation of probiotic yogurt in comparison with the standard turmeric extract (TE). The antimicrobial activity of both supplements was studied and compared in the context of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, yeasts, and fungi. The N maintains the level of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-2 in yogurt at the recommended level (7-9 log CFU/g) throughout the storage period. NOMICU® L-100 also has a higher inhibitory capacity for the growth of yeast and fungi. The evaluation of quality indicators of yogurt with N and TE at the level of 0.2% proves that yogurt with N has original taste properties. A lower degree of syneresis was noted for yogurt with TE (0.2%), but its sensory properties are unacceptable to the consumer due to the appearance of a bitter taste. In conclusion, based on the obtained results, it has been proven that the use of NOMICU® L-100 (0.2%) in the composition of yogurt provides a product of functional direction with stable quality and safety indicators, which can be stored for at least 28 days.
Keywords: antimicrobial properties; curcumin; dairy products; innovative technology; nutraceuticals.
Copyright © 2023 Buniowska-Olejnik, Urbański, Mykhalevych, Bieganowski, Znamirowska-Piotrowska, Kačániová and Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
Author JU was employed by the company Dairy Biotechnologies Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural Bioactive Compounds Enriched Functional Yogurt: Impact on the Probiotic Bacteria and Its Potential Health Benefits.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Feb 12. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10461-1. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39934501 Review.
-
Matrix Effects on the Delivery Efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 on Fecal Microbiota, Gut Transit Time, and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Healthy Young Adults.mSphere. 2021 Aug 25;6(4):e0008421. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00084-21. Epub 2021 Jul 7. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34232082 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Probiotic viability and physico-chemical and sensory properties of plain and stirred fruit yogurts made from goat's milk.Food Chem. 2012 Dec 1;135(3):1411-8. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.025. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22953874
-
Microbial, physiochemical and functional properties of probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum enriched by green tea aqueous extract.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Aug 5;9(10):5536-5545. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2512. eCollection 2021 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34646523 Free PMC article.
-
Application of natural and modified additives in yogurt formulation: types, production, and rheological and nutraceutical benefits.Front Nutr. 2023 Oct 30;10:1257439. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1257439. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38024362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Bioactive Compounds Enriched Functional Yogurt: Impact on the Probiotic Bacteria and Its Potential Health Benefits.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Feb 12. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10461-1. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39934501 Review.
-
Carrier design based on zein: From the perspectives of multi-molecule encapsulation, probiotic encapsulation, and application standards.Curr Res Food Sci. 2025 Jul 12;11:101145. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101145. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40697755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biocompatible Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Nanocapsules Enhance the Bioavailability, Antibacterial, and Immunomodulatory Activities of Curcumin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 4;25(19):10692. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910692. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409022 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing an Ex Vivo Skin Penetration Analysis Model for Predicting Ocular Drug Penetration: A Feasibility Study with Curcumin Formulations.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 6;16(10):1302. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101302. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458631 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Development and Sensory Evaluation of Extruded Snacks from Unripe Banana (Musa ABB cv. Kluai 'Namwa') and Rice Flour Enriched with Antioxidant-Rich Curcuma longa Microcapsules.Foods. 2025 Jan 10;14(2):205. doi: 10.3390/foods14020205. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39856872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behare PV, Prajapati JB. Thermization as a method for enhancing the shelf life of cultured buttermilk. Ind J Dairy Sci. (2007) 60:86–93.
-
- Brody AL. Fermented dairy packaging materials. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing; (2006). 129 p.
-
- Raju PN, Singh AK. Packaging of fermented milks and dairy products. Fermented milks and dairy products. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL: (2016) 637–671.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

