Brain Tumor Radiogenomic Classification of O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Promoter Methylation in Malignant Gliomas-Based Transfer Learning
- PMID: 37078100
- PMCID: PMC10126792
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748231169149
Brain Tumor Radiogenomic Classification of O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Promoter Methylation in Malignant Gliomas-Based Transfer Learning
Abstract
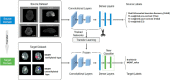
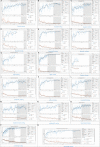
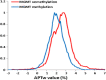
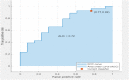
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the subject of a challenge and attention in the field of oncology and raises many promises for preventive diagnosis, but also fears, some of which are based on highly speculative visions for the classification and detection of tumors. A brain tumor that is malignant is a life-threatening disorder. Glioblastoma is the most prevalent kind of adult brain cancer and the 1 with the poorest prognosis, with a median survival time of less than a year. The presence of O6 -methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation, a particular genetic sequence seen in tumors, has been proven to be a positive prognostic indicator and a significant predictor of recurrence.This strong revival of interest in AI is modeled in particular to major technological advances which have significantly increased the performance of the predicted model for medical decision support. Establishing reliable forecasts remains a significant challenge for electronic health records (EHRs). By enhancing clinical practice, precision medicine promises to improve healthcare delivery. The goal is to produce improved prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy through evidence-based sub stratification of patients, transforming established clinical pathways to optimize care for each patient's individual requirements. The abundance of today's healthcare data, dubbed "big data," provides great resources for new knowledge discovery, potentially advancing precision treatment. The latter necessitates multidisciplinary initiatives that will use the knowledge, skills, and medical data of newly established organizations with diverse backgrounds and expertise.The aim of this paper is to use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images to train and evaluate your model to detect the presence of MGMT promoter methylation in this competition to predict the genetic subtype of glioblastoma based transfer learning. Our objective is to emphasize the basic problems in the developing disciplines of radiomics and radiogenomics, as well as to illustrate the computational challenges from the perspective of big data analytics.
Keywords: O6 -methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation; Transfer learning; artificial intelligence; big data; brain tumor; classification; radiogenomic.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improving MGMT methylation status prediction of glioblastoma through optimizing radiomics features using genetic algorithm-based machine learning approach.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 4;12(1):13412. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17707-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35927323 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation with clinical outcomes in glioblastoma and clinical strategies to modulate MGMT activity.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Sep 1;26(25):4189-99. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.5964. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18757334 Review.
-
Prediction of methylguanine methyltransferase promoter methylation in glioblastoma using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance and diffusion tensor imaging.J Neurosurg. 2014 Aug;121(2):367-73. doi: 10.3171/2014.5.JNS132279. Epub 2014 Jun 20. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 24949678
-
O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase gene promoter methylation status in gliomas and its correlation with other molecular alterations: first Indian report with review of challenges for use in customized treatment.Neurosurgery. 2010 Dec;67(6):1681-91. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e3181f743f5. Neurosurgery. 2010. PMID: 21107199 Review.
-
O6 -methylguanine DNA methyltransferase gene promoter methylation in high-grade gliomas: a review of current status.Neurol India. 2011 Mar-Apr;59(2):229-35. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.79128. Neurol India. 2011. PMID: 21483124 Review.
Cited by
-
Precision Population Cancer Medicine in Brain Tumors: A Potential Roadmap to Improve Outcomes and Strategize the Steps to Bring Interdisciplinary Interventions.Cureus. 2024 Oct 12;16(10):e71305. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71305. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39529768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive fine-tuning based transfer learning for the identification of MGMT promoter methylation status.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024 Jul 30;10(5):055018. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad6573. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024. PMID: 39029475 Free PMC article.
-
From Voxel to Gene: A Scoping Review on MRI Radiogenomics' Artificial Intelligence Predictions in Adult Gliomas and Glioblastomas-The Promise of Virtual Biopsy?Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 23;12(9):2156. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092156. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335670 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer Learning in Cancer Genetics, Mutation Detection, Gene Expression Analysis, and Syndrome Recognition.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 4;16(11):2138. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112138. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Deep Learning Models in Predicting Glioma Molecular Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;15(7):797. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070797. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mehrotra R, Ansari MA, Agrawal R, Anand RS. A transfer learning approach for AI-based classification of brain tumors. Machine Learning with Applications. 2020;2:100003. doi:10.1016/j.mlwa.2020.100003 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

