Effects of neprilysin and neprilysin inhibitors on glucose homeostasis: Controversial points and a promising arena
- PMID: 37078106
- PMCID: PMC10172023
- DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13389
Effects of neprilysin and neprilysin inhibitors on glucose homeostasis: Controversial points and a promising arena
Abstract
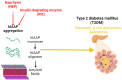
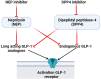
Neprilysin (NEP) is a transmembrane zinc-dependent metalloproteinase that inactivates various peptide hormones including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). NEP inhibitors may be effective in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by increasing the circulating level of GLP-1. However, acute-effect NEP inhibitors may lead to detrimental effects by increasing blood glucose independent of GLP-1. These findings suggest a controversial point regarding the potential role of NEP inhibitors on glucose homeostasis in T2DM patients. Therefore, this perspective aimed to clarify the controversial points concerning the role of NEP inhibitors on glucose homeostasis in T2DM. NEP inhibitors may lead to beneficial effects by inhibition of NEP, which is involved in the impairment of glucose homeostasis through modulation of insulin resistance. NEP increases dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) activity and contributes to increasing active GLP-1 proteolysis so NEP inhibitors may improve glycemic control through increasing endogenous GLP-1 activity and reduction of DPP4 activity. Thus, NEP inhibitors could be effective alone or in combination with antidiabetic agents in treating T2DM patients. However, long-term and short-term effects of NEP inhibitors may lead to a detrimental effect on insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis through different mechanisms including augmentation of substrates and pancreatic amyloid deposition. These findings are confirmed in animal but not in humans. In conclusion, NEP inhibitors produce beneficial rather than detrimental effects on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in humans though most of the detrimental effects of NEP inhibitors are confirmed in animal studies.
脑啡肽酶(NEP)是一种跨膜锌依赖性金属蛋白酶,可使包括胰高血糖素样肽1 (GLP-1)在内的多种肽类激素失活。NEP抑制剂可能通过提高循环GLP-1水平来有效治疗2型糖尿病(T2DM)。然而,NEP抑制剂的急性效应可能会造成血糖升高,产生有害作用,且与GLP-1无关。这些发现提示NEP抑制剂对T2DM患者血糖稳态的作用尚存有争议。本视角旨在阐明NEP抑制剂对T2DM糖稳态作用的争议点。NEP通过调节胰岛素抵抗(IR)参与糖稳态受损,NEP抑制剂可能通过抑制NEP发挥有益作用。NEP增加二肽基肽酶-4 (DPP4)活性并有助于增加GLP-1蛋白水解活性,而NEP抑制剂可能通过增加内源性GLP-1活性和降低DPP4活性来改善血糖控制。因此,NEP抑制剂可单独或联合降糖药物治疗T2DM患者。然而,NEP抑制剂的长期和短期作用机制可能不同,包括增强底物和胰腺淀粉样蛋白沉积,导致对胰岛素敏感性和葡萄糖稳态的有害影响。这些发现在动物中得到证实,但在人类中未得到证实。综上所述,NEP抑制剂对人体葡萄糖稳态和胰岛素敏感性产生有益而非有害的影响,尽管大多数有害影响已在动物研究中得到证实。.
Keywords: 2型糖尿病; neprilysin; sacubitril; type 2 diabetes mellitus; 脑啡肽酶; 脑啡肽酶抑制剂.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes published by Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of DPP-4: a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Apr;23(4):919-31. doi: 10.1185/030079906x162746. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17407649 Review.
-
Improved glycaemia in high-fat-fed neprilysin-deficient mice is associated with reduced DPP-4 activity and increased active GLP-1 levels.Diabetologia. 2017 Apr;60(4):701-708. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4172-4. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 27933334 Free PMC article.
-
Acute effects on glucose tolerance by neprilysin inhibition in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022 Oct;24(10):2017-2026. doi: 10.1111/dom.14789. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35676803 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neprilysin inhibitors and risk of Alzheimer's disease: A future perspective.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jan;28(2):e17993. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17993. Epub 2023 Oct 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37847125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neprilysin inhibition in mouse islets enhances insulin secretion in a GLP-1 receptor dependent manner.Islets. 2018;10(5):175-180. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2018.1502521. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Islets. 2018. PMID: 30142012 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The potential role of human islet amyloid polypeptide in type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's diseases.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 May 13;15(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01082-1. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 37173803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sacubitril/Valsartan Combination Partially Improves Cardiac Systolic, but Not Diastolic, Function through β-AR Responsiveness in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10617. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910617. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408945 Free PMC article.
-
Increased thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) as a possible risk factor for atherosclerosis in subclinical hypothyroidism.Thyroid Res. 2024 Jun 17;17(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13044-024-00199-3. Thyroid Res. 2024. PMID: 38880884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) inhibitors in Parkinson disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(11):e18412. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18412. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38842132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive review on neprilysin (NEP) inhibitors: design, structure-activity relationships, and clinical applications.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1501407. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1501407. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39764460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Anand IS, et al. Angiotensin–neprilysin inhibition in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(17):1609‐1620. - PubMed
-
- Pardossi‐Piquard R, Dunys J, Yu G, St. George‐Hyslop P, Alves da Costa C, Checler F. Neprilysin activity and expression are controlled by nicastrin. J Neurochem. 2006;97(4):1052‐1056. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

