Threshold of Main Pancreatic Duct Diameter in Identifying Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm by Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- PMID: 37078135
- PMCID: PMC10126643
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338231170942
Threshold of Main Pancreatic Duct Diameter in Identifying Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm by Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
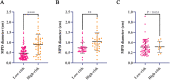
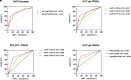
Objective: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a rare pancreatic lesion. The identification of malignancy is critical for the establishment of treatment strategies. Main pancreatic duct (MPD) diameter is one critical feature for malignant IPMNs. However, the threshold of 1.0 cm is challenged. In this study, we explored independent risk factors and further calculated the threshold of MPD in identifying malignant IPMNs. Method: A total of 151 IPMN patients were included in this retrospective study. Demographic information, clinicopathological features, laboratory testing, and preoperative radiological characteristics by magnetic resonance imaging were collected. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were performed to determine the MPD diameter's cutoff levels and evaluate the predicted factors' diagnostic ability. Results: A cutoff value of 0.77 cm MPD (an area under the curve (AUC) = 0.746) in all IPMNs and 0.82 cm (AUC = 0.742) in the main duct involved IPMNs was obtained. MPD diameter (odds ratio (OR), 12.67; 95% confidence interval (CI), 4.80-33.48) and the mural nodule (OR, 12.98; 95% CI, 3.18-52.97) were the independent associated factors with high-risk IPMNs. The combined model with MPD and mural nodule showed a better predictive performance than mural nodule or MPD diameter alone (AUC = 0.803 vs 0.619, 0.746). A nomogram was developed and showed good performance (C index = 0.803). Conclusion: Our data show that mural nodule and MPD diameter are independent risk factors in identifying malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. A cutoff value of 0.77 cm of MPD diameter may be a threshold value in identifying malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms or undergoing surgical resection.
Keywords: intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; main pancreatic duct; mural nodule; risk factor; threshold.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An imaging-based model to predict the malignant potential of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.Eur Radiol. 2025 Feb;35(2):700-711. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11003-z. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39112752
-
Threshold of main pancreatic duct for malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm at head-neck and body-tail.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 19;22(1):473. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02577-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36402960 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of a Revised Management Strategy for Patients With Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms Involving the Main Pancreatic Duct.JAMA Surg. 2017 Jan 18;152(1):e163349. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2016.3349. Epub 2017 Jan 18. JAMA Surg. 2017. PMID: 27829085
-
Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance image for malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: the importance of size of enhancing mural nodule within cyst.Jpn J Radiol. 2022 Dec;40(12):1282-1289. doi: 10.1007/s11604-022-01312-y. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Jpn J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35781178 Review.
-
Imaging Features for Predicting High-Grade Dysplasia or Malignancy in Branch Duct Type Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2022 Feb;29(2):1297-1312. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-10662-2. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34554343
Cited by
-
An imaging-based model to predict the malignant potential of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.Eur Radiol. 2025 Feb;35(2):700-711. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11003-z. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39112752
-
Pancreatic Cancer: A Review of Risk Factors.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;14(8):980. doi: 10.3390/life14080980. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202722 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Attiyeh MA, Fernández-Del Castillo C, Al Efishat M, et al.Development and validation of a multi-institutional preoperative nomogram for predicting grade of dysplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 2018;267(1):157-163. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000002015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

