Impact of aging on immune function in the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases: potential for therapeutic targets
- PMID: 37078192
- PMCID: PMC10330361
- DOI: 10.1080/17476348.2023.2205127
Impact of aging on immune function in the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases: potential for therapeutic targets
Abstract
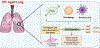
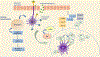
Introduction: Several immunological alterations that occur during pulmonary diseases often mimic alterations observed in the aged lung. From the molecular perspective, pulmonary diseases and aging partake in familiar mechanisms associated with significant dysregulation of the immune systems. Here, we summarized the findings of how aging alters immunity to respiratory conditions to identify age-impacted pathways and mechanisms that contribute to the development of pulmonary diseases.
Areas covered: The current review examines the impact of age-related molecular alterations in the aged immune system during various lung diseases, such as COPD, IPF, Asthma, and alongside many others that could possibly improve on current therapeutic interventions. Moreover, our increased understanding of this phenomenon may play a primary role in shaping immunomodulatory strategies to boost outcomes in the elderly. Here, the authors present new insights into the context of lung-related diseases and describe the alterations in the functioning of immune cells during various pulmonary conditions altered with age.
Expert opinion: The expert opinion provided the concepts on how aging alters immunity during pulmonary conditions, and suggests the associated mechanisms during the development of lung diseases. As a result, it becomes important to comprehend the complex mechanism of aging in the immune lung system.
Keywords: Aging; COPD; Cellular senescence; Cytokines; IPF; Immunity; Lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures


References
-
- Hernandez-Gonzalez F, et al. Chapter 3 - Lung aging and senescence in health and disease, in Cellular Senescence in Disease. Serrano M and Muñoz-Espín D, Editors. 2022; Academic Press. 61–80.
-
- Brandenberger C and Mühlfeld C. Mechanisms of lung aging. Cell Tissue Res. 2017; 367(3): 469–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
