Orelabrutinib for the treatment of relapsed or refractory MCL: a phase 1/2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm study
- PMID: 37078706
- PMCID: PMC10432605
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009168
Orelabrutinib for the treatment of relapsed or refractory MCL: a phase 1/2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm study
Abstract
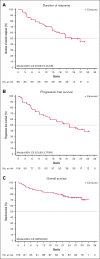
Relapsed or refractory (r/r) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an aggressive B-cell malignancy with a poor prognosis. Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a mediator of B-cell receptor signaling and is associated with the development of B-cell lymphomas. Patients with r/r MCL were enrolled in this phase 1/2 study and treated with orelabrutinib, a novel, highly selective BTK inhibitor. The median number of prior regimens was 2 (range, 1-4). The median age was 62 years (range, 37-73 years). Eligible patients received oral orelabrutinib 150 mg once daily (n = 86) or 100 mg twice daily (n = 20) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. A dose of 150 mg once daily was chosen as the preferred recommended phase 2 dose. After a median follow-up duration of 23.8 months, the overall response rate was 81.1%, with 27.4% achieving a complete response and 53.8% achieving a partial response. The median duration of response and progression-free survival were 22.9 and 22.0 months, respectively. The median overall survival (OS) was not reached, and the rate of OS at 24 months was 74.3%. Adverse events (AEs) occurring in >20% of patients were thrombocytopenia (34.0%), upper respiratory tract infection (27.4%), and neutropenia (24.5%). Grade ≥3 AEs were infrequent and most commonly included thrombocytopenia (13.2%), neutropenia (8.5%), and anemia (7.5%). Three patients discontinued treatment because of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), but no fatal TRAEs were reported. Orelabrutinib showed substantial efficacy and was well tolerated in patients with r/r MCL. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT03494179.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: X.-Y.Z., R.-B.Z., B.Z., and Y.-M.T. are employees of InnoCare Pharma Limited. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Teras LR, DeSantis CE, Cerhan JR, Morton LM, Jemal A, Flowers CR. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(6):443–459. - PubMed
-
- Vose JM. Mantle cell lymphoma: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and clinical management. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(8):806–813. - PubMed
-
- Cheah CY, Seymour JF, Wang ML. Mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(11):1256–1269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

