Efficacy of oblique lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37079105
- PMCID: PMC10449690
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-023-04880-4
Efficacy of oblique lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: This meta-analysis aimed to compare the differences in postoperative efficacy between oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases.
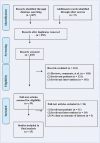
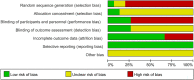
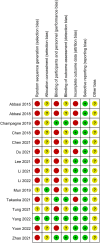
Materials and methods: Strictly based on the search strategy, we searched the published papers on OLIF and TLIF for the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases in PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and Cochrane Library. A total of 607 related papers were retrieved, and 15 articles were finally included. The quality of the papers was evaluated according to the Cochrane systematic review methodology, and the data were extracted and meta-analyzed using Review manager 5.4 software.
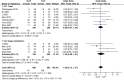
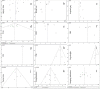
Results: Through comparison, it was found that in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases, the OLIF group had certain advantages over the TLIF group in terms of intraoperative blood loss, hospital stay, visual analog scale (VAS) for leg pain (VAS-LP), Oswestry disability index (ODI), disc height (DH), foraminal height (FH), fused segmental lordosis (FSL), and cage height, and the differences were statistically significant. The results were similar in terms of surgery time, complications, fusion rate, VAS for back pain (VAS-BP) and various sagittal imaging indicators, and there was no significant difference.
Conclusions: OLIF and TLIF can relieve low back pain symptoms in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases, but OLIF has certain advantages in terms of ODI and VAS-LP. In addition, OLIF has the advantages of minor intraoperative trauma and quick postoperative recovery.
Keywords: Lumbar degenerative diseases; Meta; OLIF; TLIF.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







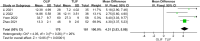
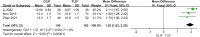


Similar articles
-
Effect of Approach Based Lumbar Interbody Fusion on Sagittal Spinopelvic Parameters and Functional Outcomes: Comparison between Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF) and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF).Indian J Orthop. 2024 Oct 3;59(1):40-46. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01229-w. eCollection 2025 Jan. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39735873
-
A systematic review of anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF), transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), posterolateral lumbar fusion (PLF).Eur Spine J. 2023 Jun;32(6):1911-1926. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-07567-x. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Eur Spine J. 2023. PMID: 37071155
-
Clinical outcomes after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and lateral lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2018 Jul;41(3):755-770. doi: 10.1007/s10143-016-0806-8. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Neurosurg Rev. 2018. PMID: 28013419
-
Minimally invasive versus mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in managing low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024 Sep 12;166(1):365. doi: 10.1007/s00701-024-06231-7. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024. PMID: 39264454 Free PMC article.
-
Early radiological adjacent segment changes following L4/5 fusion: a retrospective comparative study of oblique lateral interbody fusion and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.PeerJ. 2025 Aug 21;13:e19918. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19918. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40860655 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of PE-PLIF with a novel ULBD approach for lumbar degeneration diseases: a large-channel endoscopic retrospective study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Apr 29;19(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04755-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38685055 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Approach Based Lumbar Interbody Fusion on Sagittal Spinopelvic Parameters and Functional Outcomes: Comparison between Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF) and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF).Indian J Orthop. 2024 Oct 3;59(1):40-46. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01229-w. eCollection 2025 Jan. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39735873
-
Current Trends and Future Directions in Lumbar Spine Surgery: A Review of Emerging Techniques and Evolving Management Paradigms.J Clin Med. 2025 May 13;14(10):3390. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103390. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomechanical evaluation of different oblique lumbar interbody fusion constructs: a finite element analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jan 27;25(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07204-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38279094 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion rate and complications of oblique lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis.Front Surg. 2024 Apr 30;11:1374134. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1374134. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 38746621 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

