Ferulic Acid Improves Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Impairments by Alleviating the PP2B/DARPP-32/PP1 Axis-Mediated STEP Increase and Aβ Burden in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 37079191
- PMCID: PMC10457275
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-023-01356-6
Ferulic Acid Improves Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Impairments by Alleviating the PP2B/DARPP-32/PP1 Axis-Mediated STEP Increase and Aβ Burden in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
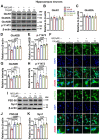
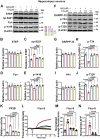
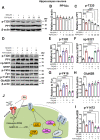
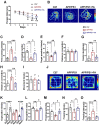
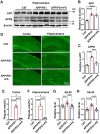
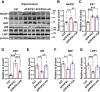
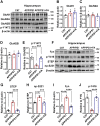
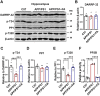
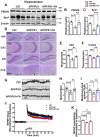
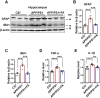
The burden of Alzheimer's disease, the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease, is increasing exponentially due to the increase in the elderly population worldwide. Synaptic plasticity is the basis of learning and memory, but it is impaired in AD. Uncovering the disease's underlying molecular pathogenic mechanisms involving synaptic plasticity could lead to the identification of targets for better disease management. Using primary neurons treated with Aβ and APP/PS1 animal models, we evaluated the effect of the phenolic compound ferulic acid (FA) on synaptic dysregulations. Aβ led to synaptic plasticity and cognitive impairments by increasing STEP activity and decreasing the phosphorylation of the GluN2B subunit of NMDA receptors, as well as decreasing other synaptic proteins, including PSD-95 and synapsin1. Interestingly, FA attenuated the Aβ-upregulated intracellular calcium and thus resulted in a decrease in PP2B-induced activation of DARPP-32, inhibiting PP1. This cascade event maintained STEP in its inactive state, thereby preventing the loss of GluN2B phosphorylation. This was accompanied by an increase in PSD-95 and synapsin1, improved LTP, and a decreased Aβ load, together leading to improved behavioral and cognitive functions in APP/PS1 mice treated with FA. This study provides insight into the potential use of FA as a therapeutic strategy in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cognitive impairment; Ferulic acid; Increased intracellular calcium; PP2B/DARPP-32/PP1 axis; Synapses.
© 2023. The American Society for Experimental Neurotherapeutics, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corilagin improves cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice by reducing Aβ generation and enhancing synaptic plasticity.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 15;981:176893. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176893. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39134295
-
Moringa Oleifera Alleviates Aβ Burden and Improves Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Impairments in APP/PS1 Mice.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 14;14(20):4284. doi: 10.3390/nu14204284. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36296969 Free PMC article.
-
Huatuo Zaizao pill ameliorates cognitive impairment of APP/PS1 transgenic mice by improving synaptic plasticity and reducing Aβ deposition.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 May 29;18(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2237-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29843688 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2014 Nov 14;9:48. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-48. Mol Neurodegener. 2014. PMID: 25394486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presenilins and APP in neuritic and synaptic plasticity: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Neuromolecular Med. 2002;2(2):167-96. doi: 10.1385/NMM:2:2:167. Neuromolecular Med. 2002. PMID: 12428810 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications of Lysosomal Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 13;21(3):1014-1031. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.103028. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An In Vivo C57BL/6 Mouse Study Demonstrating Fine-Tuning of Serum and Brain-Derived Exosomes Reveal Therapeutic Potential of Phytochemical Ferulic Acid Against Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun 4. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05096-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40467939
-
Jiawei Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill (JKZP) Alleviates Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion-Induced Hippocampal Synaptic Damage via S100A10/tPA/BDNF Pathway.Brain Behav. 2025 Feb;15(2):e70328. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70328. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 39957398 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the neuropathology and memory decline induced by monosodium glutamate in the Alzheimer's disease-like animal model.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 24;14:1283440. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1283440. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37942488 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the improvement of cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice by danggui shaoyao san and its disassembled prescriptions through modulation of the gut microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1620784. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1620784. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40822397 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

