Risk Factors for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Mediated Cardiovascular Toxicities
- PMID: 37079251
- PMCID: PMC10256640
- DOI: 10.1007/s11912-023-01414-4
Risk Factors for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Mediated Cardiovascular Toxicities
Abstract
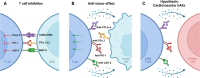
Purpose of review: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have improved the field of cancer, especially in patients with advanced malignancies. Nevertheless, cardiovascular immune-related adverse events (irAEs) with high mortality and morbidity have been observed, including myocarditis, pericarditis, and vasculitis. To date, only a few clinical risk factors have been described and are currently being investigated.
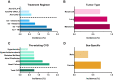
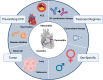
Recent findings: In this review, we address the four most prevailing risk factors for cardiovascular irAEs. ICI combination therapy is a predominant risk factor for developing ICI-mediated myocarditis. Additionally, ICI combined with other anti-cancer treatments (e.g., tyrosine kinase inhibitors, radiation, chemotherapy) seems to increase the risk of developing cardiovascular irAEs. Other risk factors include female sex, pre-existing cardiovascular disease, and specific tumors, on which we will further elaborate in this review. An a priori risk strategy to determine who is at risk to develop these cardiovascular irAEs is needed. Insights into the impact of risk factors are therefore warranted to help clinicians improve care and disease management in these patients.
Keywords: ICI; Myocarditis; Pericarditis; Risk factors; Vasculitis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-organ Immune-Related Adverse Event Is a Risk Factor of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Myocarditis in Cancer Patients: A Multi-center Study.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 18;13:879900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.879900. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35924238 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: an observational, retrospective, pharmacovigilance study.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Dec;19(12):1579-1589. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30608-9. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30442497 Free PMC article.
-
Major Adverse Cardiac Events With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Pooled Analysis of Trials Sponsored by the National Cancer Institute-Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program.J Clin Oncol. 2022 Oct 10;40(29):3439-3452. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00369. Epub 2022 Jun 4. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35658474 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotoxicity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.Curr Oncol Rep. 2021 May 3;23(7):79. doi: 10.1007/s11912-021-01070-6. Curr Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33937956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor cardiotoxicity: Breaking barriers in the cardiovascular immune landscape.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021 Nov;160:121-127. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.07.006. Epub 2021 Jul 22. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34303670 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling immune checkpoint inhibitor associated myocarditis in vitro and its therapeutic implications.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2024 Dec;10:100122. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2024.100122. Epub 2024 Nov 20. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2024. PMID: 39742339 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular adverse events in patients with lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a nationwide database study.Oncologist. 2025 Jun 4;30(6):oyaf151. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyaf151. Oncologist. 2025. PMID: 40549047 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors and cardiovascular toxicity: immunology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025 Jul 17. doi: 10.1007/s11239-025-03146-7. Online ahead of print. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025. PMID: 40673965 Review.
-
High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with cancer therapy-related cardiovascular toxicity in high-risk cancer patients under immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.Clin Res Cardiol. 2024 Feb;113(2):301-312. doi: 10.1007/s00392-023-02327-9. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Clin Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37955712 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical mouse models of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2025 May;4(5):526-538. doi: 10.1038/s44161-025-00640-2. Epub 2025 May 7. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2025. PMID: 40335724 Review.
References
-
- Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2521–2532. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, et al. Updated analysis of KEYNOTE-024: pembrolizumab versus platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score of 50% or greater. Faculty Sci Med Health - Papers: Part B. 2019;37:537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

