Indirect treatment comparison of lurbinectedin versus other second-line treatments for small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 37079341
- PMCID: PMC10402758
- DOI: 10.57264/cer-2022-0098
Indirect treatment comparison of lurbinectedin versus other second-line treatments for small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
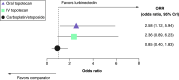
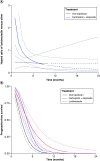
Aim: Compare lurbinectedin versus other second-line (2L) small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) treatments. Methods: An unanchored matching-adjusted indirect comparison connected the platinum-sensitive SCLC cohort of a single-arm lurbinectedin trial to a network of three randomized controlled trials (oral and intravenous [IV] topotecan, and platinum re-challenge) identified by systematic literature review. Network meta-analysis methods estimated relative treatment effects. Results: In platinum-sensitive patients, lurbinectedin demonstrated a survival benefit and favorable safety profile versus oral and IV topotecan and platinum re-challenge (overall survival, hazard ratio [HR]: 0.43; 95% credible interval [CrI]: 0.27, 0.67; HR: 0.43; 95% CrI: 0.26, 0.70; HR: 0.42; 95% CrI: 0.30, 0.58 respectively). Conclusion: Lurbinectedin showed a robust survival benefit and favorable safety versus other SCLC treatments in 2L platinum-sensitive SCLC.
Keywords: lurbinectedin; matching-adjusted indirect comparison; network meta-analysis; platinum sensitive; small-cell lung cancer; topotecan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Van Meerbeeck JP, Fennell DA, De Ruysscher DK. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 378(9804), 1741–1755 (2011). - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Comprehensive Network. Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2023. In: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) (2022). www.nccn.org
-
- Augert A, Macpherson D. Treating transcriptional addiction in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 26(6), 783–784 (2014). - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2022. American Cancer Society, GA, USA: (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
