Use of Intracameral Tissue Plasminogen Activator During Uveitic Cataract Surgery
- PMID: 37079881
- PMCID: PMC10587359
- DOI: 10.1080/09273948.2023.2194410
Use of Intracameral Tissue Plasminogen Activator During Uveitic Cataract Surgery
Abstract
Purpose: To report the outcomes of intracameral tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) use during uveitic cataract surgery.
Design: Retrospective case series from a single United States tertiary center of 36 eyes from 31 consecutive patients with established uveitis who received intraoperative intracameral tPA during cataract surgery between 2016 and 2020.
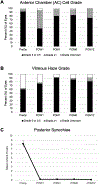
Results: Mean visual acuity (VA) improved from logMAR 1.0 ± 0.7 preoperatively to logMAR 0.7 ± 0.8 by POM12. VA improved from baseline postoperatively (POM1 p = 0.0002, POM6 p = 0.006 and POM12 p = 0.007). Minimal to no anterior chamber inflammation was achieved in 47.2% of the eyes by POW1 and 80.0% of the eyes by POM1. Mean clock-hours of posterior synechiae improved from 8.2 ± 3.8 preoperatively to 0.1 ± 0.6 by POM12. Six eyes developed hyphema and/or vitreous hemorrhage, four of which resolved spontaneously.
Conclusions: Adjunctive intracameral tPA during uveitic cataract surgery improves VA and intraocular inflammation, but risks postoperative hemorrhage. Intraoperative tPA as adjunctive anti-inflammatory therapy warrants randomized prospective studies.
Keywords: Cataract surgery; intraocular inflammation; postoperative inflammation; tissue plasminogen activator; uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures
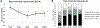

Similar articles
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs versus corticosteroids for controlling inflammation after uncomplicated cataract surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 3;7(7):CD010516. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010516.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28670710 Free PMC article.
-
Use of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rTPA) for treatment of fibrin in the anterior chamber of the horse.Vet Med Sci. 2024 Jul;10(4):e1448. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1448. Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38818763 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative antibiotics for prevention of acute endophthalmitis after cataract surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 13;2(2):CD006364. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006364.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28192644 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic Intracameral Antibiotics and Endophthalmitis After Cataract Surgery.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug 1;142(8):699-706. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.1716. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38900438 Free PMC article.
-
Trifocal intraocular lenses versus bifocal intraocular lenses after cataract extraction among participants with presbyopia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 27;1(1):CD012648. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012648.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36705482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geanon JD, Tripathi BJ, Tripathi RC, Barlow GH. Tissue plasminogen activator in avascular tissues of the eye: a quantitative study of its activity in the cornea, lens, and aqueous and vitreous humors of dog, calf, and monkey. Exp Eye Res. 1987;44(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(87)80025-8 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
