Head-to-head comparison of magnetic resonance elastography-based liver stiffness, fat fraction, and T1 relaxation time in identifying at-risk NASH
- PMID: 37080558
- PMCID: PMC10521779
- DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000417
Head-to-head comparison of magnetic resonance elastography-based liver stiffness, fat fraction, and T1 relaxation time in identifying at-risk NASH
Abstract
Background and aims: The presence of at-risk NASH is associated with an increased risk of cirrhosis and complications. Therefore, noninvasive identification of at-risk NASH with an accurate biomarker is a critical need for pharmacologic therapy. We aim to explore the performance of several magnetic resonance (MR)-based imaging parameters in diagnosing at-risk NASH.
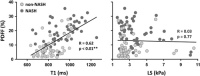
Approach and results: This prospective clinical trial (NCT02565446) includes 104 paired MR examinations and liver biopsies performed in patients with suspected or diagnosed NAFLD. Magnetic resonance elastography-assessed liver stiffness (LS), 6-point Dixon-derived proton density fat fraction (PDFF), and single-point saturation-recovery acquisition-calculated T1 relaxation time were explored. Among all predictors, LS showed the significantly highest accuracy in diagnosing at-risk NASH [AUC LS : 0.89 (0.82, 0.95), AUC PDFF : 0.70 (0.58, 0.81), AUC T1 : 0.72 (0.61, 0.82), z -score test z >1.96 for LS vs any of others]. The optimal cutoff value of LS to identify at-risk NASH patients was 3.3 kPa (sensitivity: 79%, specificity: 82%, negative predictive value: 91%), whereas the optimal cutoff value of T1 was 850 ms (sensitivity: 75%, specificity: 63%, and negative predictive value: 87%). PDFF had the highest performance in diagnosing NASH with any fibrosis stage [AUC PDFF : 0.82 (0.72, 0.91), AUC LS : 0.73 (0.63, 0.84), AUC T1 : 0.72 (0.61, 0.83), |z| <1.96 for all].
Conclusion: Magnetic resonance elastography-assessed LS alone outperformed PDFF, and T1 in identifying patients with at-risk NASH for therapeutic trials.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Study design, database creation, and data acquisition: Jiahui Li, Xin Lu, and Zheng Zhu. Manuscript preparation: Jiahui Li, Xin Lu, Alina M. Allen, and Meng Yin. Statistical analysis: Jiahui Li and Kyle J. Kalutkiewicz. Statistical review: Terry M. Therneau. Critical revision of the manuscript: Jiahui Li, Terry M. Therneau, Richard L. Ehman, Alina M. Allen, and Meng Yin. Imaging review: Safa Hoodeshenas, Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, and Taofic Mounajjed. Technical/material support: Yi Sui, Kevin J. Glaser, Armando Manduca, Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, Vijay H. Shah, Richard L. Ehman, Alina M. Allen, and Meng Yin. Study concept and design, database creation, funding obtainment, and study supervision: Vijay H. Shah, Richard L. Ehman, Alina M. Allen, and Meng Yin.
Kyle J. Kalutkiewicz is employed by and consults for Resoundant, Inc. Kevin J. Glaser owns stock in and intellectual property rights with Resoundant, Inc. Armando Manduca owns stock in Resoundant, Inc. Richard L. Ehman owns stock in, owns intellectual property rights with, and received grants from Resoundant, Inc. Alina M. Allen consults for, advises, and received grants from Novo Nordisk. She received grants from Pfizer and Target Pharma. Meng Yin owns stock in and intellectual property rights with Resoundant, Inc. The remaining authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures



Comment in
-
Role of HNF4alpha-cMyc interaction in liver regeneration and recovery after acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury.Hepatology. 2023 Oct 1;78(4):1106-1117. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000367. Epub 2023 Apr 7. Hepatology. 2023. PMID: 37021787 Free PMC article.
-
The role of MRI technology in liver evaluation for NAFLD patients: Advancements and opportunities.Hepatology. 2023 Oct 1;78(4):1020-1022. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000478. Epub 2023 May 23. Hepatology. 2023. PMID: 37212150 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sepanlou SG, Safiri S, Bisignano C, Ikuta KS, Merat S, Saberifiroozi M, et al. . The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:245–66. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rowe IA, Parker R. The diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease should carry important prognostic information. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:449–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

