Fluoroscopy- and CT-Guided Gold Fiducial Marker Placement for Intraoperative Localization during Spinal Surgery: Review of 179 Cases at a Single Institution-Technique and Safety Profile
- PMID: 37080723
- PMCID: PMC10171395
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A7854
Fluoroscopy- and CT-Guided Gold Fiducial Marker Placement for Intraoperative Localization during Spinal Surgery: Review of 179 Cases at a Single Institution-Technique and Safety Profile
Abstract
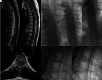
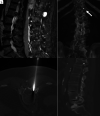
Background and purpose: Wrong-level spinal surgery, especially in the thoracic spine, remains a challenge for a variety of reasons related to visualization, such as osteopenia, large body habitus, severe kyphosis, radiographic misinterpretation, or anatomic variation. Preoperative fiducial marker placement performed in a dedicated imaging suite has been proposed to facilitate identification of thoracic spine vertebral levels. In this current study, we report our experience using image-guided percutaneous gold fiducial marker placement to enhance the accuracy and safety of thoracic spinal surgical procedures.
Materials and methods: A retrospective review was performed of all fluoroscopy- or CT-guided gold fiducial markers placed at our institution between January 3, 2019, and March 16, 2022. A chart review of 179 patients was performed detailing the procedural approach and clinical information. In addition, the method of gold fiducial marker placement (fluoroscopy/CT), procedure duration, spinal level of the gold fiducial marker, radiation dose, fluoroscopy time, surgery date, and complications (including whether wrong-level surgery occurred) were recorded.
Results: A total of 179 patients (104 female) underwent gold fiducial marker placement. The mean age was 57 years (range, 12-96 years). Fiducial marker placement was performed by 13 different neuroradiologists. All placements were technically successful without complications. All 179 (100%) operations were performed at the correct level. Most fiducial markers (143) were placed with fluoroscopy with the most common location at T6-T8. The most common location for placement in CT was at T3 and T4.
Conclusions: All operations guided with gold fiducial markers were performed at the correct level. There were no complications of fiducial marker placement.
© 2023 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of Wrong-level Surgery in the Thoracic Spine: Preoperative Computer Tomography Fluoroscopy-guided Percutaneous Gold Fiducial Marker Placement in 57 Patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020 Dec 15;45(24):1720-1724. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003691. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020. PMID: 32925684
-
Avoidance of wrong-level thoracic spine surgery: intraoperative localization with preoperative percutaneous fiducial screw placement.J Neurosurg Spine. 2012 Mar;16(3):280-4. doi: 10.3171/2011.3.SPINE10445. Epub 2011 Nov 4. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012. PMID: 22054638
-
Thoracic spine localization using preoperative placement of fiducial markers and subsequent CT. A technical report.J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2015 Jan;76(1):66-71. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1371512. Epub 2014 Jul 21. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25045861
-
Planting the seeds of success: CT-guided gold seed fiducial marker placement to guide robotic radiosurgery.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2013 Apr;57(2):207-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1754-9485.2012.02445.x. Epub 2012 Sep 21. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23551782 Review.
-
Intraoperative spinal navigation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003 Aug 1;28(15 Suppl):S54-61. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000076899.78522.D9. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. PMID: 12897475 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and deployment of robots in a bronchoscopy suite.Breathe (Sheff). 2025 Jul 15;21(3):240247. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0247-2024. eCollection 2025 Jul. Breathe (Sheff). 2025. PMID: 40673070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
