RBM4 dictates ESCC cell fate switch from cellular senescence to glutamine-addiction survival through inhibiting LKB1-AMPK-axis
- PMID: 37080995
- PMCID: PMC10119322
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01367-x
RBM4 dictates ESCC cell fate switch from cellular senescence to glutamine-addiction survival through inhibiting LKB1-AMPK-axis
Abstract
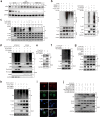
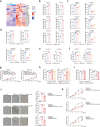
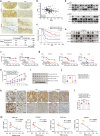
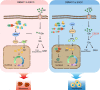
Cellular senescence provides a protective barrier against tumorigenesis in precancerous or normal tissues upon distinct stressors. However, the detailed mechanisms by which tumor cells evade premature senescence to malignant progression remain largely elusive. Here we reported that RBM4 adversely impacted cellular senescence to favor glutamine-dependent survival of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells by dictating the activity of LKB1, a critical governor of cancer metabolism. The level of RBM4 was specifically elevated in ESCC compared to normal tissues, and RBM4 overexpression promoted the malignant phenotype. RBM4 contributed to overcome H-RAS- or doxorubicin-induced senescence, while its depletion caused P27-dependent senescence and proliferation arrest by activating LKB1-AMPK-mTOR cascade. Mechanistically, RBM4 competitively bound LKB1 to disrupt the LKB1/STRAD/MO25 heterotrimeric complex, subsequently recruiting the E3 ligase TRIM26 to LKB1, promoting LKB1 ubiquitination and degradation in nucleus. Therefore, such molecular process leads to bypassing senescence and sustaining cell proliferation through the activation of glutamine metabolism. Clinically, the ESCC patients with high RBM4 and low LKB1 have significantly worse overall survival than those with low RBM4 and high LKB1. The RBM4 high/LKB1 low expression confers increased sensitivity of ESCC cells to glutaminase inhibitor CB-839, providing a novel insight into mechanisms underlying the glutamine-dependency to improve the efficacy of glutamine inhibitors in ESCC therapeutics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SIRT1 promotes proliferation and prevents senescence through targeting LKB1 in primary porcine aortic endothelial cells.Circ Res. 2010 Apr 30;106(8):1384-93. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.215483. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20203304
-
Circ_0001093 promotes glutamine metabolism and cancer progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting miR-579-3p/glutaminase axis.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2022 Apr;54(2):119-134. doi: 10.1007/s10863-022-09935-6. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2022. PMID: 35322289
-
Regulation of Hippo/YAP signaling and Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma progression by an E3 ubiquitin ligase PARK2.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 25;10(21):9443-9457. doi: 10.7150/thno.46078. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32863938 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1 deficiency-induced metabolic reprogramming in tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic diseases.Mol Metab. 2021 Feb;44:101131. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101131. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33278637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPKα-like proteins as LKB1 downstream targets in cell physiology and cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 May;99(5):651-662. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02040-y. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33661342 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning developed LKB1-AMPK signaling related signature for prognosis and drug sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20738. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08583-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594698 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic modeling and Emerging therapeutic targets Unveiled through single-cell sequencing in esophageal squamous Cell carcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 21;10(19):e38078. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38078. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39397956 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2 promotes the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via HuR-mediated mRNA stabilization.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Oct;14(10):4329-4344. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.07.022. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39525580 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous RBM4 prevents Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via downregulating the expression of PTBP1.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Aug 7;57(3):365-377. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024103. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39118568 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of genetic associations and single-cell expression profiles reveals potential links between migraine and multiple diseases: a phenome-wide association study.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1301208. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1301208. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38385040 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

