Epigenetic investigation into circulating microRNA 197-3p in sera from patients affected by malignant pleural mesothelioma and workers ex-exposed to asbestos
- PMID: 37081052
- PMCID: PMC10119131
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33116-z
Epigenetic investigation into circulating microRNA 197-3p in sera from patients affected by malignant pleural mesothelioma and workers ex-exposed to asbestos
Abstract
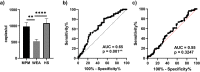
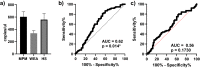
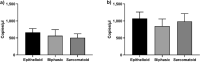
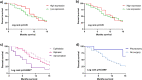
The epigenetic role of microRNAs is established at both physiological and pathological levels. Dysregulated miRNAs and their targets appear to be a promising approach for innovative anticancer therapies. In our previous study, circulating miR-197-3p tested dysregulated in workers ex-exposed to asbestos (WEA). Herein, an epigenetic investigation on this circulating miRNA was carried out in sera from malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) patients. MiR-197-3p was quantified in MPM (n = 75) sera and comparatively analyzed to WEA (n = 75) and healthy subject (n = 75) sera, using ddPCR and RT-qPCR techniques. Clinicopathological characteristics, occupational, non-occupational information and overall survival (OS) were evaluated in correlation studies. MiR-197-3p levels, analyzed by ddPCR, were significantly higher in MPM than in WEA cohort, with a mean copies/µl of 981.7 and 525.01, respectively. Consistently, RT-qPCR showed higher miR-197-3p levels in sera from MPM with a mean copies/µl of 603.7, compared to WEA with 336.1 copies/µl. OS data were significantly associated with histologic subtype and pleurectomy. Circulating miR-197-3p is proposed as a new potential biomarker for an early diagnosis of the MPM onset. Indeed, miR-197-3p epigenetic investigations along with chest X-ray, computed tomography scan and spirometry could provide relevant information useful to reach an early and effective diagnosis for MPM.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The following authors: G.D.M., F.F., E.T., E.M., R.L., F.M., I.B., and M.T. declare that data from this study has been employed, in part, for the Italian patent application number RBI17430-IT. M.R.I., A.C., C.M., F.G., V.E. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

