E3 ubiquitin ligase on the biological properties of hematopoietic stem cell
- PMID: 37081103
- PMCID: PMC10163092
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-023-02315-6
E3 ubiquitin ligase on the biological properties of hematopoietic stem cell
Abstract
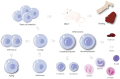
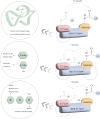
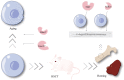
Hematopoietic stem cells are a group of heterogeneity cells with the potential to differentiate into various types of mature blood cells. Their basic biological properties include quiescence, self-renewal, multilineage differentiation, and homing ability, with the homing of exogenous hematopoietic stem cells after transplantation becoming a new focus, while the first three properties share some similarity in mechanism due to connectivity. In various complex mechanisms, the role of E3 ubiquitin ligases in hematopoietic homeostasis and malignant transformation is receiving increasing attention. As a unique part, E3 ubiquitin ligases play an important role in physiological regulation mechanism of posttranslational modification. In this review, we focus on the recent progress of the crucial role of E3 ubiquitin ligases that target specific proteins for ubiquitination to regulate biological properties of hematopoietic stem cells. Additionally, this paper deals with E3 ubiquitin ligases that affect the biological properties through aging and summarizes the relevant applications of targeting E3 ligases in hematopoietic malignancies. We present some ideas on the clinical application of E3 ubiquitin ligase to regulate hematopoietic stem cells and also believe that it is meaningful to study the upstream signal of these E3 ubiquitin ligases because hematopoietic stem cell dysfunction is caused by deficiency of some E3 ligases.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligases; Hematopoietic stem cell; Homing ability; Lineage differentiation; Quiescence; Self-renewal.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer stem cells: key regulators of cancer hallmarks and novel therapeutic opportunities.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023 Jun;46(3):545-570. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00777-x. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 36745329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of the HECT E3 ubiquitin ligases in gastric cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Feb 7;29:1610931. doi: 10.3389/pore.2023.1610931. eCollection 2023. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 36825281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory role of E3 ubiquitin ligases in normal B lymphopoiesis and B-cell malignancies.Life Sci. 2023 Oct 15;331:122043. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122043. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37633415 Review.
-
Regulation of Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis by FBOX Ubiquitin E3 Ligases.Trends Immunol. 2020 Dec;41(12):1128-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33160841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of E3 ligases in the ubiquitin-dependent regulation of spermatogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Jun;30:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24632385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The autocrine motility factor receptor delays the pathological progression of Alzheimer's disease via regulating the ubiquitination-mediated degradation of APP.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Apr 29;17(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01741-7. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40301979 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell profiling unveils a geroprotective role of Procyanidin C1 in hematopoietic immune system via senolytic and senomorphic effects.NPJ Aging. 2025 May 2;11(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41514-025-00222-3. NPJ Aging. 2025. PMID: 40316527 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

